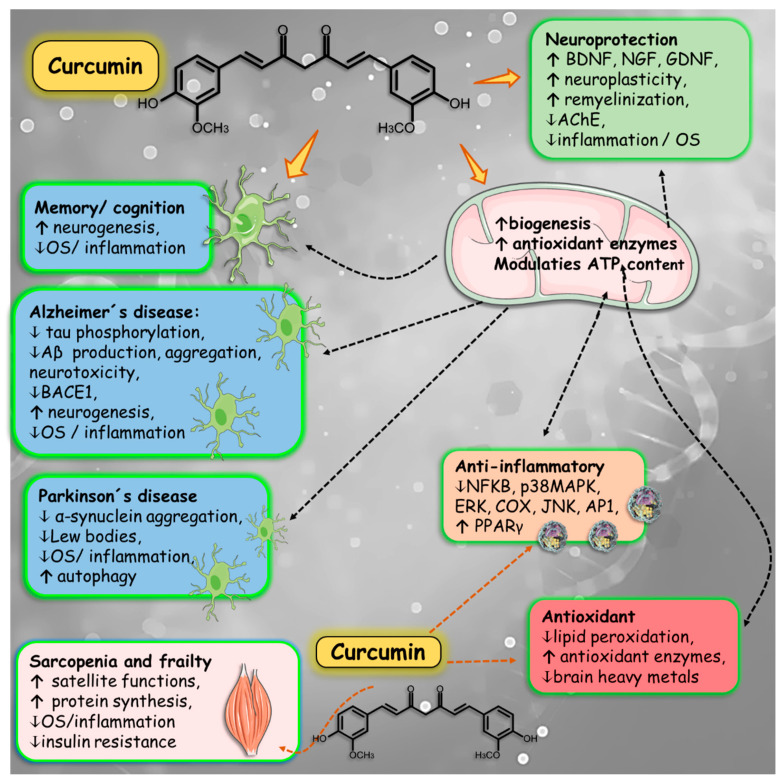
Figure 7.
Summary of curcumin effects on some aging-related conditions. Curcumin possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that are related to the prevention or treatment of memory loss, neurodegenerative diseases, sarcopenia, and frailty. These effects can play a role in mitochondrial functions that, on the other hand, are also associated with diminishing oxidative stress and inflammation. The results are associated with an increase in the synthesis of neuronal growth factors such as BDNF, NGF, and GDNF, an increase in neuroplasticity, reduction in brain neuroinflammation, and restoration of brain functions. In muscles, there is an increase in protein synthesis and a reduction in its degradation. AChE: acetylcholine esterase; AP-1: activator protein-1; BACE1: β-secretase 1; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; COX: cyclooxygenase; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GDNF: glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; NGF: nerve growth factor; NF-κB nuclear factor kappa beta; p38MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PPAR-γ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.