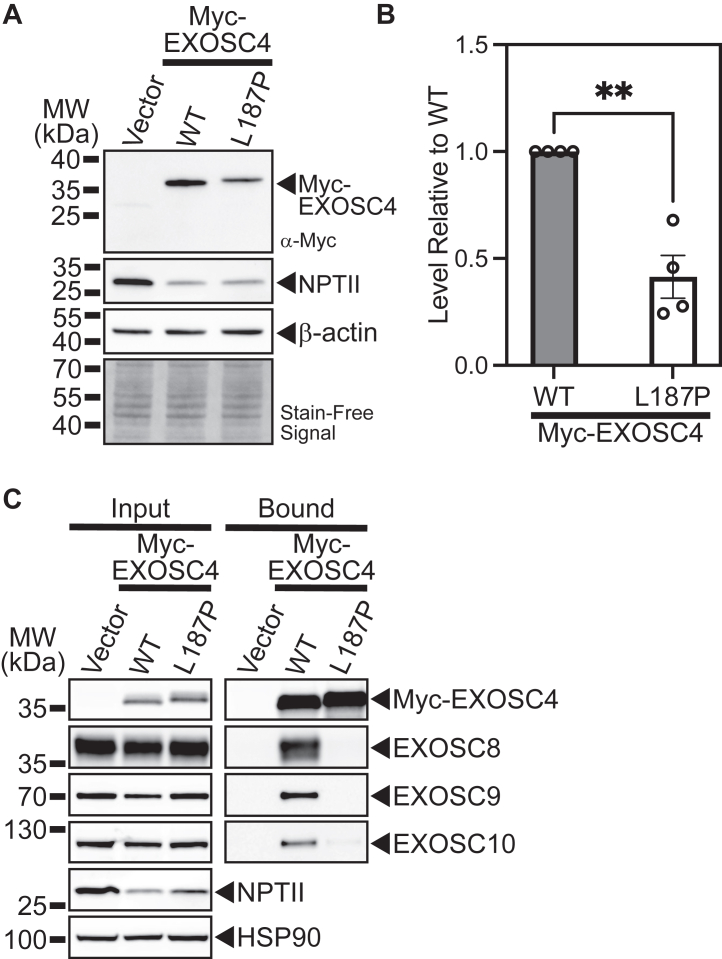
Figure 7.
The pathogenic amino acid substitution in EXOSC4decreases the steady-state level of the protein andcan alter interactions with other RNA exosome subunits.A, the murine EXOSC4-L187P variant, corresponding to the human EXOSC4 variant identified in patients, is present at a lower steady-state level than WT murine EXOSC4 in a mouse neuronal cell line. Lysates of mouse N2a cells transfected with empty vector or vector expressing murine Myc-EXOSC4 or Myc-EXOSC4-L187P were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibody to detect Myc-EXOSC4 proteins. The stain-free signal serves as a loading control and neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPTII) serves as a transfection control. B, quantitation of the relative level of EXOSC4-L187P protein compared to EXOSC4 detected in the lysates of N2a cells expressing Myc-tagged EXOSC4 or EXOSC4-L187P from four immunoblot experiments – one shown in (A). The graph shows the relative level of EXOSC4-Myc protein compared to WT EXOSC4 (WT) from four independent experiments (n = 4). Error bars represent SEM. Statistical significance is calculated by a Student’s t test (∗∗p-value ≤ 0.01). C, Myc-EXOSC4 or Myc-EXOSC4-L187P was immunoprecipitated from N2a cells and interactions with the RNA exosome subunits EXOSC8, EXOSC9, and the RNA exosome–associated EXOSC10 were analyzed by immunoblotting. Both the input and bound samples are shown for Myc-EXOSC4 and Myc-EXOSC4-L187P. NPTII represents the neomycin phosphotransferase II, which is encoded on the Myc-EXOSC4/EXOSC4-L187P plasmids, indicating similar levels of transfection for EXOSC4 and EXOSC4-L187P. Hsp90 serves as a loading control.