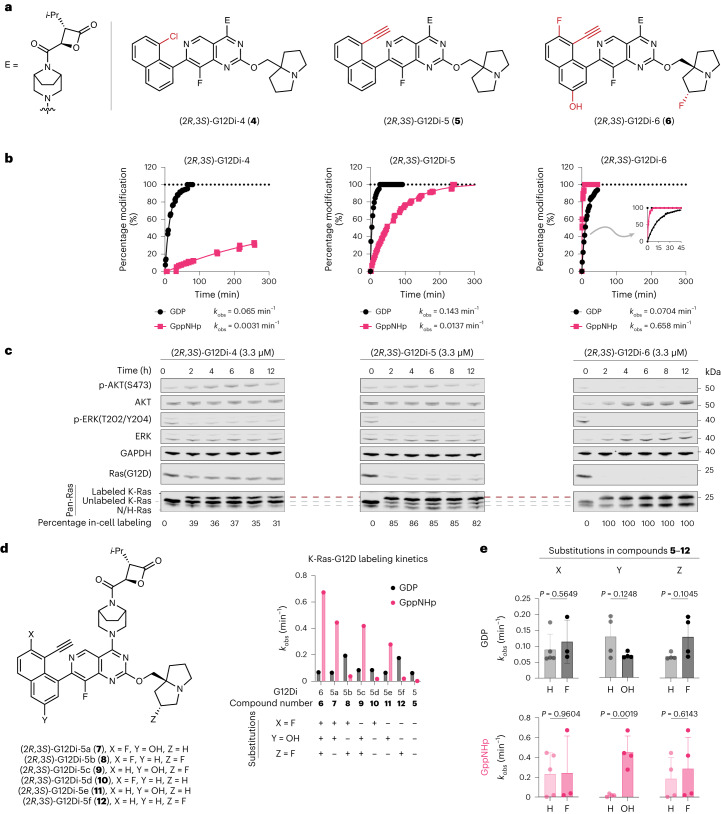
Fig. 3. Rapid covalent modification of K-Ras-G12D•GTP is essential for in-cell target engagement and oncogenic signaling suppression.
a, Chemical structures of (2R,3S)-G12Di-4 (4), (2R,3S)-G12Di-5 (5) and (2R,3S)-G12Di-6 (6). b, Recombinant K-Ras-G12D (200 nM) labeling kinetics with 3-isopropyl malolactones (10 µM) (n = 3, replicates are plotted as individual data points). c, Western blot time course of cellular K-Ras-G12D covalent engagement and downstream signaling inhibition. Data are representative of two independent experiments. d, Covalent K-Ras-G12D labeling kinetics in both nucleotides by (2R,3S)-G12Di-5, (2R,3S)-G12Di-6 and (2R,3S)-G12Di-5a–5f (7–12). Substitutions X, Y and Z vary between compounds 7–12. e, Analysis of the determining substitution on covalent labeling kinetics by an unpaired t-test comparing X = H (n = 5) or F (n = 3), Y = H (n = 4) or OH (n = 4), and Z = H (n = 4) or F (n = 4). All data points represent individual chemical compound. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.