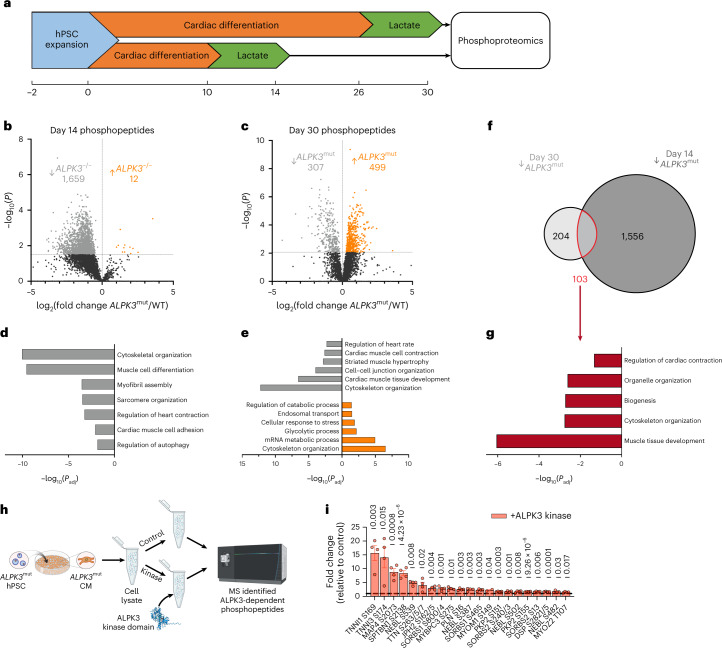
Fig. 4. ALPK3 is critical for phosphorylation of sarcomeric and autophagy components.
a, Experimental outline of the phosphoproteomic experiments; n = 5 independent differentiations per group. b, Volcano plot of day 14 WT and ALPK3mut hPSC CMs to show differential abundance of normalized phosphopeptides. c, Volcano plot of WT and ALPK3mut hPSC CMs to show the differential abundance of normalized phosphopeptides at day 30. d, GO terms of biological processes enriched in differentially phosphorylated proteins between day 14 WT and ALPK3mut hPSC CMs. e, GO terms of biological processes enriched in differentially phosphorylated proteins between day 30 WT and ALPK3mut hPSC CMs. f, Venn diagram showing the overlap of dephosphorylated phosphopeptides in ALPK3mut hPSC CMs between day 14 and day 30. g, GO terms of biological processes enriched in commonly dephosphorylated proteins in ALPK3mut hPSC CMs between day 14 and day 30. h, Schematic of ALPK3 global kinase assay performed in ALPK3mut hPSC CMs. i, Cytoskeletal and contractile proteins with elevated phosphopeptide abundance after the ALPK3 kinase assay. n = 2–4 per condition. The dashed bar indicates that the control value = 1. Values represent unadjusted P values from a two-sided t-test. Data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m.