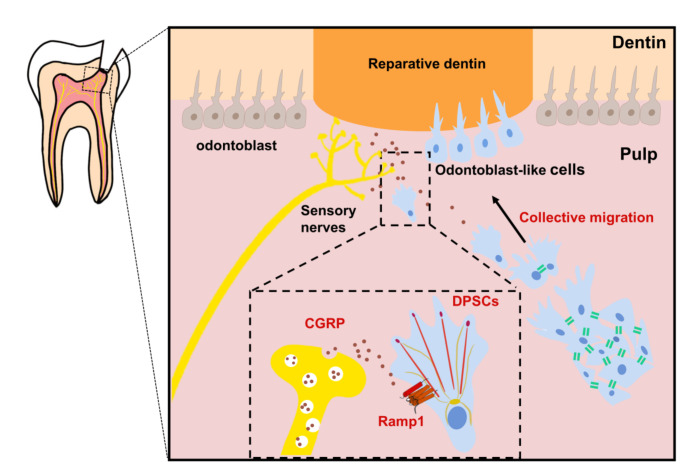
Fig. 7.
Sensory nerves foster pulp healing by regulating the collective migration of DPSCs through the CGRP-Ramp1 axis. In the dental pulp, nerve fibers are organized into bundles within the root canal, branching out in the crown pulp, and forming a dense network beneath the odontoblast layer. Sensory nerves are the main constituent of nerves in the dental pulp, which can sense various outer stimuli. After pulp injury, the sensory nerves exhibit a rapid response and sprouting. Concurrently, CGRP is released from sensory nerves near the injury site to act on the receptor Ramp1 on the surface of the activated DPSCs, thereby facilitating the collective cell migration of DPSCs to the injury site by promoting cell polarization and intercellular junctions, thus contributing to the repair of pulp injury