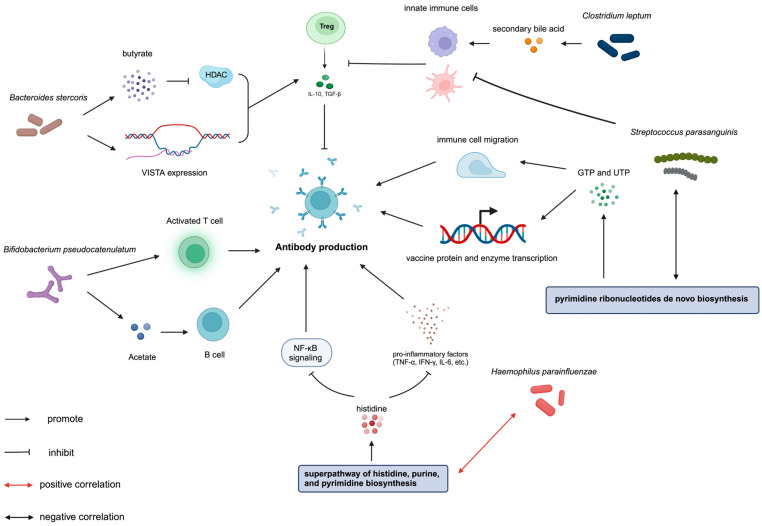
Figure 3.
Graphical illustration of the relationship between gut microbiota, metabolic pathways, and BNT162b2 immunogenicity after three doses: insights from our research and prior literature; Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum can produce acetate to activate B cells as well as increase the proportion of activated T cells. Bacteroides stercoris secretes butyrate as HDAC inhibitor and promotes the expression of VISTA gene to prompt Treg cell function. Streptococcus parasanguinis enhances the production of IL-10 by facilitating the function of innate immune cells, which activates Treg cells. Clostridium leptum can convert primary bile acids to secondary bile acids and facilitate the innate immune response. Haemophilus parainfluenzae was positively correlated with the superpathway of histidine, purine, and pyrimidine biosynthesis. Histidine, produced by the superpathway of histidine, purine, and pyrimidine biosynthesis, decreases the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-6, and inhibits NF-κB signaling. NF-κB signaling plays a key role in the immune reaction to vaccines by mediating the maturation and activation of T cells and B cells. The superpathway of pyrimidine ribonucleotides in de novo biosynthesis can produce CTP and UTP to stimulate immune cell migration and translate mRNA vaccines and enzymes. Abbreviations: HDAC, histone deacetylase; VISTA, V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T cell activation; IL-10, interleukin 10; Treg cells, T regulator cells; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ, Interferon-γ; IL-6, Interleukin 6; CTP, cytidine triphosphate; UTP, uridine 5–triphosphate.