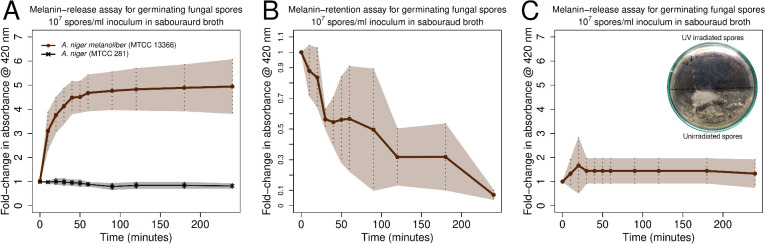
Figure 2.
Peptidomelanin release assay for Aspergillus spps. spores. (A) A. niger melanoliber (MTCC 13366) and A. niger (MTCC 281) spores were inoculated into Sabouraud broth. A. niger melanoliber rapidly released soluble peptidomelanin into the medium. In contrast, A. niger released no soluble peptidomelanin into the medium. (B) Peptidomelanin retention assay for A. niger melanoliber spores in Sabouraud broth. At predetermined time points, samples were isolated and fixed using 8% glutaraldehyde to halt peptidomelanin release. Samples were treated with 0.1 M NaOH to release retained peptidomelanin. Retained peptidomelanin decreased with time, indicating that new peptidomelanin is not synthesized during germination, and only existing peptidomelanin is released. 0.1 M NaOH did not degrade peptidomelain for the duration of incubation (Figure S4). (C) Melanin release assay for UV-irradiated A. niger melanoliber spores. Irradiated spores did not release peptidomelanin into the Sabouraud broth, demonstrating that only live spores release melanin. (Inset) Petri plate confirming UV irradiated spores do not germinate. All experiments were performed in quadruplicate. Lines represent means. The shaded area represents standard deviation.