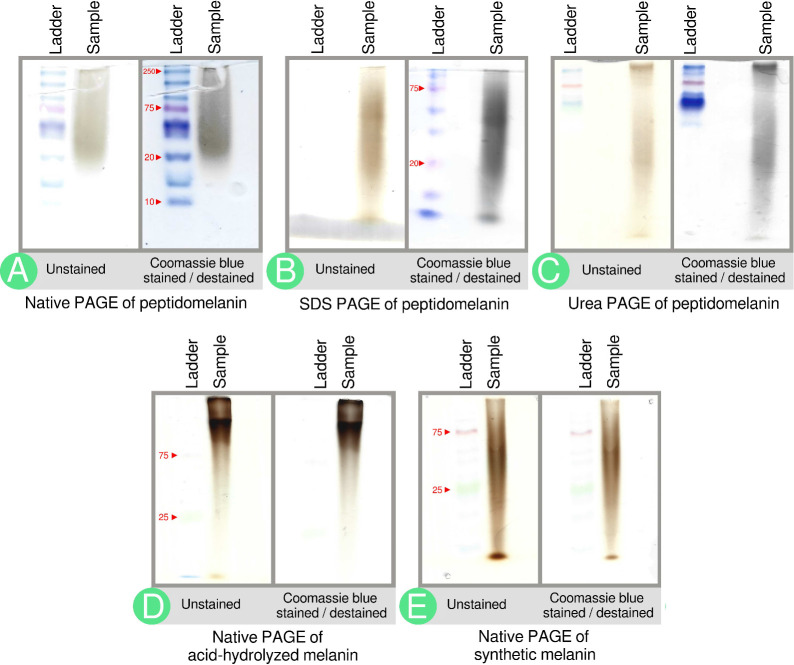
Figure 4.
PAGE gels indicate the biochemical composition of peptidomelanin. (A) Native PAGE of peptidomelanin. A brown smear from ∼20 to ≥250 kDa is observed. Coomassie blue staining darkens the smear, indicating the presence of an amino acid component. (B) SDS PAGE and (C) 8 M Urea PAGE of peptidomelanin. Coomassie blue staining reveals that the amino acid component does not separate from the melanin component, indicating a covalent linkage between the two components (ladder not resolved). The observation of smears rather than discrete bands on gels A–C confirms that peptidomelanin is an amorphous polymer. (D) Native PAGE of resolubilized acid-hydrolyzed melanin displays a smear that runs slower on a gel. The smear was only marginally stained by Coomassie blue. Both these observations indicate the loss of the amino acid component upon acid-hydrolysis. (E) Native PAGE of synthetic L-DOPA melanin. The smear does not uptake Coomassie blue as it lacks an amino acid component.