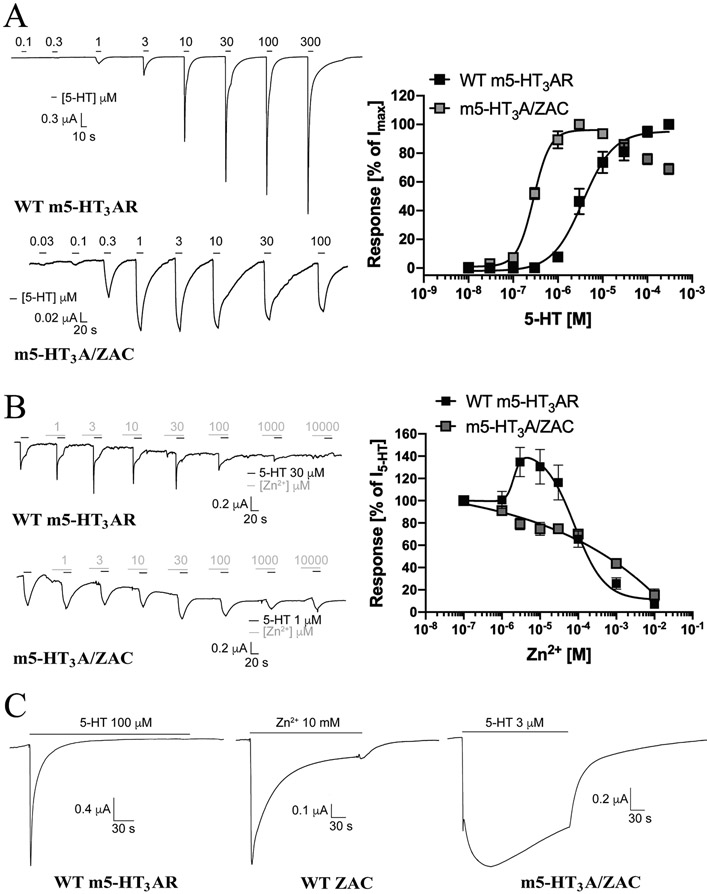
Fig. 2. Functional properties exhibited by the chimeric m5-HT3A/ZAC receptor.
A. Agonist properties displayed by 5-HT at m5-HT3A/ZAC. Representative traces for 5-HT-evoked currents in WT m5-HT3AR- and m5-HT3A/ZAC-expressing oocytes (left) and averaged concentration-response relationships displayed by 5-HT at WT m5-HT3AR and m5-HT3A/ZAC (means ± S.E.M., n = 7–9) (right). B. Modulatory properties displayed by Zn2+ at m5-HT3A/ZAC. Representative traces for the Zn2+-mediated modulation of 5-HT (EC80)-evoked currents in WT m5-HT3AR- and m5-HT3A/ZAC-expressing oocytes (left) and averaged concentration-effect relationships displayed by Zn2+ at the 5-HT (EC80)-mediated currents through WT m5-HT3AR and m5-HT3A/ZAC (means ± S.E.M., n = 7–8) (right). 5-HT (30 μM) and 5-HT (1 μM) were used for WT m5-HT3AR and m5-HT3A/ZAC, respectively. C. Representative traces of the currents evoked by 4 min-applications of saturating agonist concentrations at WT m5-HT3AR-, WT ZAC- and m5-HT3A/ZAC-expressing oocytes. 5-HT (100 μM), Zn2+ (10 mM) and 5-HT (3 μM) were used at WT m5-HT3AR, WT ZAC and m5-HT3A/ZAC, respectively.