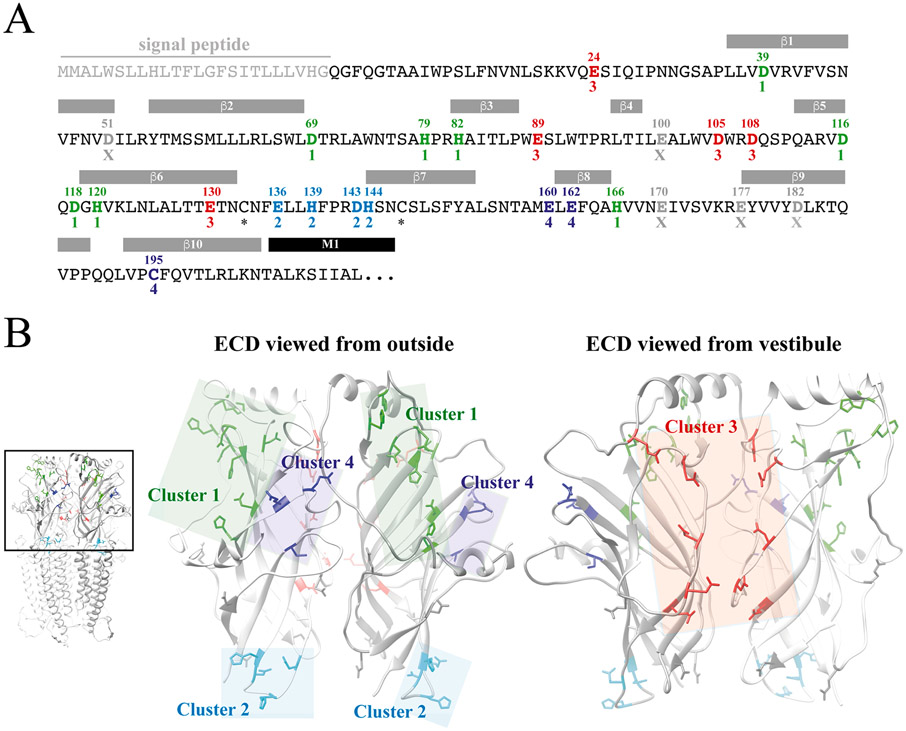
Fig. 5. Candidate Zn2+-binding residues in the extracellular domain of ZAC.
A. Amino acid sequence of the ZAC ECD. The indicated signal peptide, the β-sheet β1-β10 and the M1 α-helix segments in ZAC are predicted based on amino acid sequence aligment of the ZAC and m5-HT3A subunits and these segments in the m5-HT3AR cryo-EM structure (PDB ID: 6HIN) [11]. The 25 candidate Zn2+-binding residues in the ZAC ECD are given in bold with their residue numbers above. The candidate Zn2+-binding residues in the four defined clusters are given (Cluster 1: green; Cluster 2: cyan; Cluster 3: red; Cluster 4: dark-blue), with the five candidate residues not included in a cluster given in grey (“X”), and the two cysteines forming the Cys-loop are indicated with asterisks. B. Homology model of ZAC based on the cryo-EM structure of m5-HT3AR (PDB ID: 6HIN). The pentameric ZAC complex (left) and the ECD for two neighbouring subunits in the ZAC complex viewed from the outside (middle) and from the vestibule (right). The candidate Zn2+-binding residues in this domain defined as Cluster 1 (green), Cluster 2 (cyan), Cluster 3 (red) and Cluster 4 (dark-blue) are indicated in the ECD dimer, with the five candidate residues not included in a cluster shown in grey.