Abstract
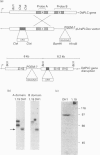
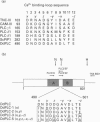
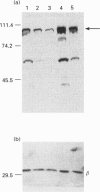
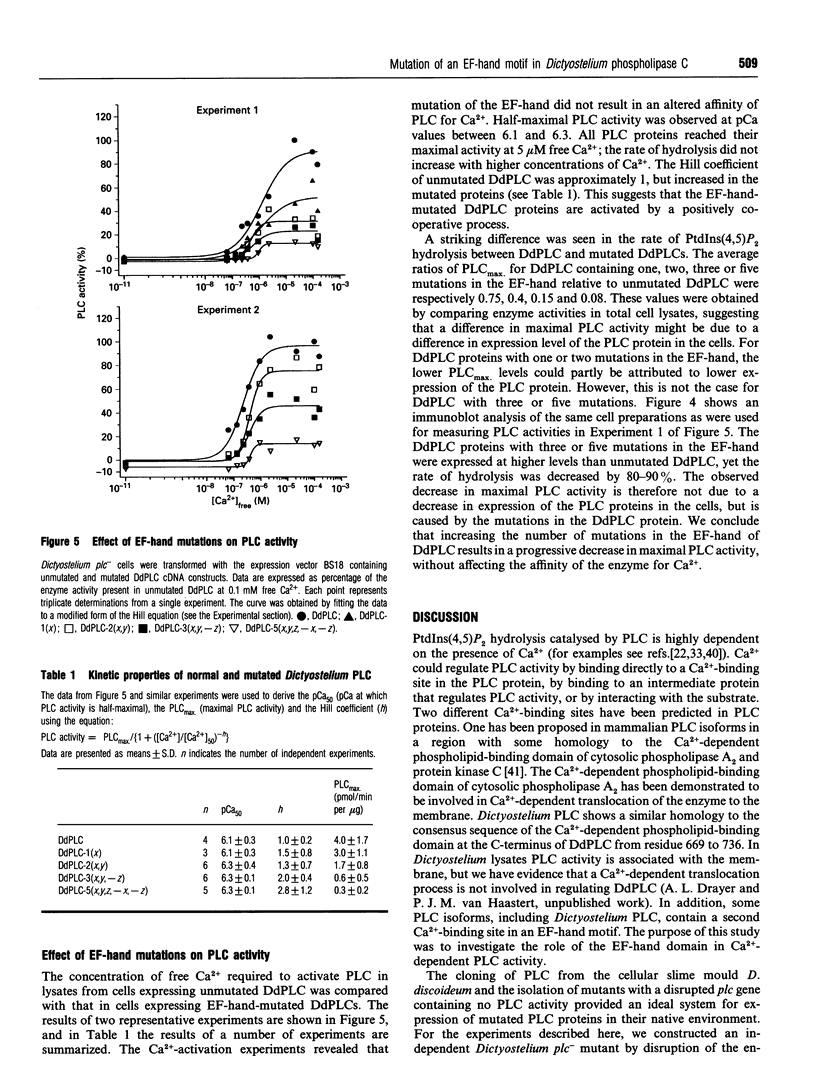
Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC) is dependent on Ca2+ ions for substrate hydrolysis. The role of an EF-hand Ca(2+)-binding motif in Ca(2+)-dependent PLC activity was investigated by site-directed mutagenesis of the Dictyostelium discoideum PLC enzyme. Amino acid residues with oxygen-containing side chains at co-ordinates x, y, z, -x and -z of the putative Ca(2+)-binding-loop sequence were replaced by isoleucine (x), valine (y) or alanine (z, -x and -z). The mutated proteins were expressed in a Dictyostelium cell line with a disrupted plc gene displaying no endogenous PLC activity, and PLC activity was measured in cell lysates at different Ca2+ concentrations. Replacement of aspartate at position x, which is considered to play an essential role in Ca2+ binding, had little effect on Ca2+ affinity and maximal enzyme activity. A mutant with substitutions at both aspartate residues in position x and y also showed no decrease in Ca2+ affinity, whereas the maximal PLC activity was reduced by 60%. Introduction of additional mutations in the EF-hand revealed that the Ca2+ concentration giving half-maximal activity was unaltered, but PLC activity levels at saturating Ca2+ concentrations were markedly decreased. The results demonstrate that, although the EF-hand domain is required for enzyme activity, it is not the site that regulates the Ca(2+)-dependence of the PLC reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bairoch A., Cox J. A. EF-hand motifs in inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):454–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. The PROSITE dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins, its current status. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3097–3103. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Rotin D., Batzer A., Mandiyan V., Schlessinger J. SH3 domains direct cellular localization of signaling molecules. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T. Preparation of metal-chelate complexes and the design of steady-state kinetic experiments involving metal nucleotide complexes. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:219–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bominaar A. A., Kesbeke F., Van Haastert P. J. Phospholipase C in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cyclic AMP surface receptor and G-protein-regulated activity in vitro. Biochem J. 1994 Jan 1;297(Pt 1):181–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2970181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boy-Marcotte E., Vilaine F., Camonis J., Jacquet M. A DNA sequence from Dictyostelium discoideum complements ura3 and ura5 mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):406–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00382076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Hou C., Sidiropoulos D., Stock J. B., Jakobs K. H., Gierschik P. Stimulation of phospholipase C by guanine-nucleotide-binding protein beta gamma subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):821–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes M. E., Honkanen L., Rebecchi M. J. Proteolytic fragments of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1. Catalytic and membrane binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11586–11593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer A. L., Van der Kaay J., Mayr G. W., Van Haastert P. J. Role of phospholipase C in Dictyostelium: formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and normal development in cells lacking phospholipase C activity. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1601–1609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer A. L., van Haastert P. J. Molecular cloning and expression of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18387–18392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. V., Carne A., Katan M. Structural requirements of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C delta 1 for enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):339–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Kessin R. A defined minimal medium for axenic strains of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Emori Y. A dual functional signal mediator showing RhoGAP and phospholipase C-delta stimulating activities. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):286–291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. K., Ahern K. G., Firtel R. A. Establishment of a transient expression system for Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2613–2623. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A. Phosphoinositides and calcium as regulators of cellular actin assembly and disassembly. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:169–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Parker P. J. Purification of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from a particulate fraction of bovine brain. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Nockolds C. E. Carp muscle calcium-binding protein. II. Structure determination and general description. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3313–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly P., Wu L., Welker D. L., Devreotes P. N. A G-protein beta-subunit is essential for Dictyostelium development. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):986–995. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrief N. D., Kretsinger R. H., Goodman M. Evolution of EF-hand calcium-modulated proteins. I. Relationships based on amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jun;30(6):522–562. doi: 10.1007/BF02101108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D., Jhon D. Y., Lee C. W., Ryu S. H., Rhee S. G. Removal of the carboxyl-terminal region of phospholipase C-beta 1 by calpain abolishes activation by G alpha q. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3710–3714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. E., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. A mutation in PLC1, a candidate phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, causes aberrant mitotic chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4351–4364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:951–998. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijken P., Lammers A. A., Van Haastert P. J. In Dictyostelium discoideum inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate is dephosphorylated by a 3-phosphatase and a 1-phosphatase. Biochem J. 1995 May 15;308(Pt 1):127–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. J., Ashworth J. M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1190171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Hofmann A., Köppel B., Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. The Ca(2+)-binding domains in non-muscle type alpha-actinin: biochemical and genetic analysis. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):599–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Jiang H., Katz A., Simon M. I. Identification of critical regions on phospholipase C-beta 1 required for activation by G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3704–3709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Katz A., Simon M. I. Activation of phospholipase C beta 2 by the alpha and beta gamma subunits of trimeric GTP-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoko-o T., Matsui Y., Yagisawa H., Nojima H., Uno I., Toh-e A. The putative phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gene, PLC1, of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]