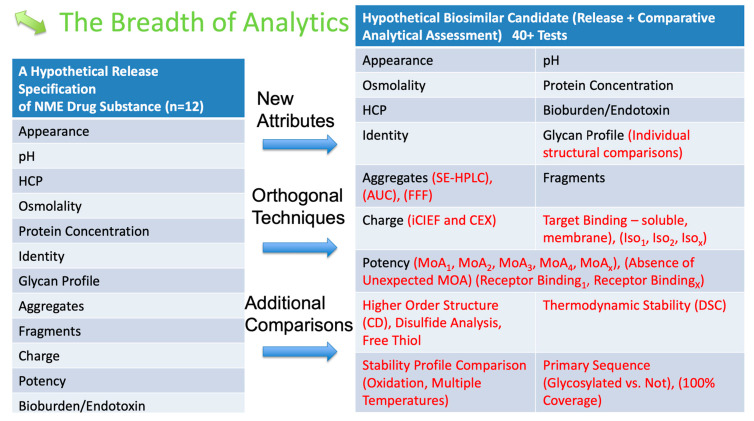
Figure 2.
FDA-proposed testing of biosimilars to establish analytical similarity [38]. Items in red show new suggestions by the FDA. Host–Cell Proteins (HCPs) are proteins produced by the host organism (often bacteria, yeast, or mammalian cells) used to produce recombinant proteins or biologics. HCP analysis is crucial to minimize these proteins in the final product to avoid immune responses in patients. Size-Exclusion High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (SE-HPLC) is a chromatography method that separates molecules based on size. It is used to analyze the molecular weight distribution of proteins and detect aggregates in biopharmaceuticals. Analytical Ultracentrifugation (AUC) is a technique that uses high-speed centrifugation to measure the sedimentation properties of particles in solution. It characterizes macromolecules according to proteins’ size, shape, and interactions. Field-flow fractionation (FFF) is a separation technique that separates and characterizes macromolecules, nanoparticles, and colloids based on their size and molecular weight. It is used in the analysis of complex biological samples. Imaged Capillary Isoelectric Focusing (iCIEF) is a technique used to separate proteins based on their isoelectric point (pI) within a capillary tube. This method is valuable for assessing the charge heterogeneity of protein therapeutics. Cation Exchange Chromatography (CEX) is an ion exchange chromatography where positively charged ions (cations) are separated based on their affinity to the negatively charged stationary phase. It is commonly used to purify proteins and analyze their charge variants. Mechanism of Action (MoA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. Understanding the MoA is crucial in the development and characterization of biological drugs. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) is a thermal–analytical technique for studying proteins’ thermal stability and folding/unfolding properties. It measures the heat flow associated with thermal transitions in a sample.