Abstract
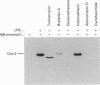
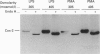
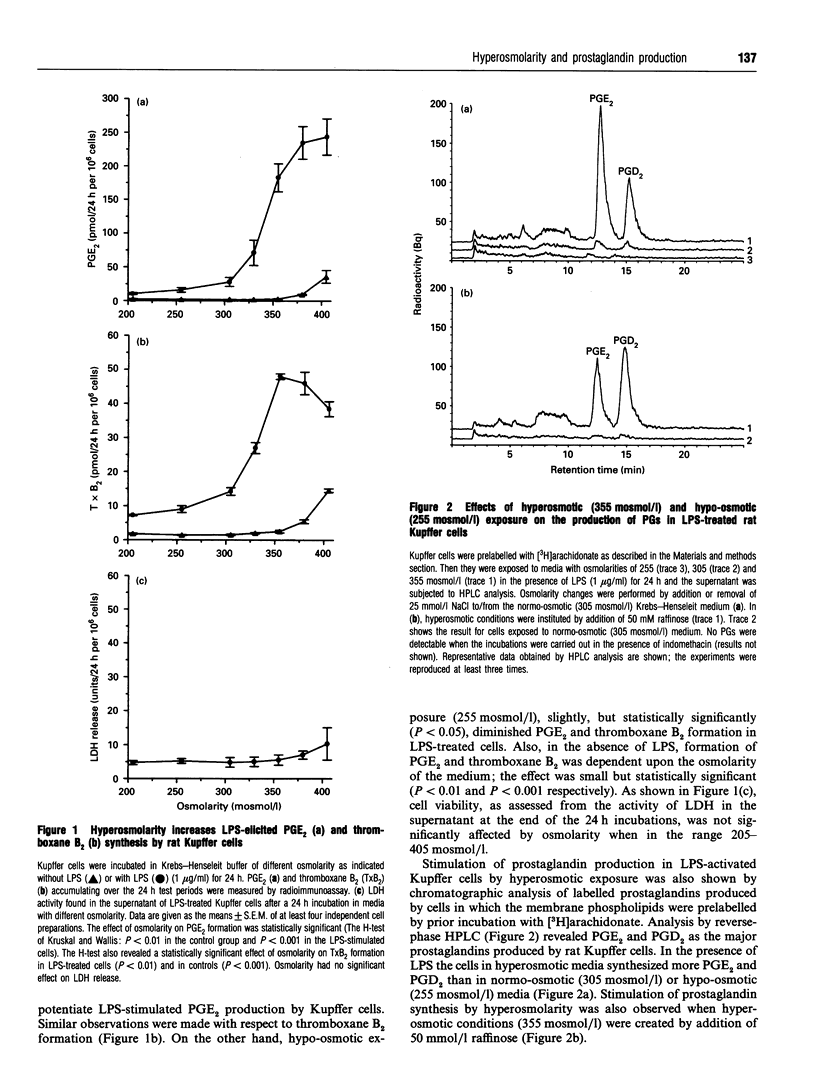
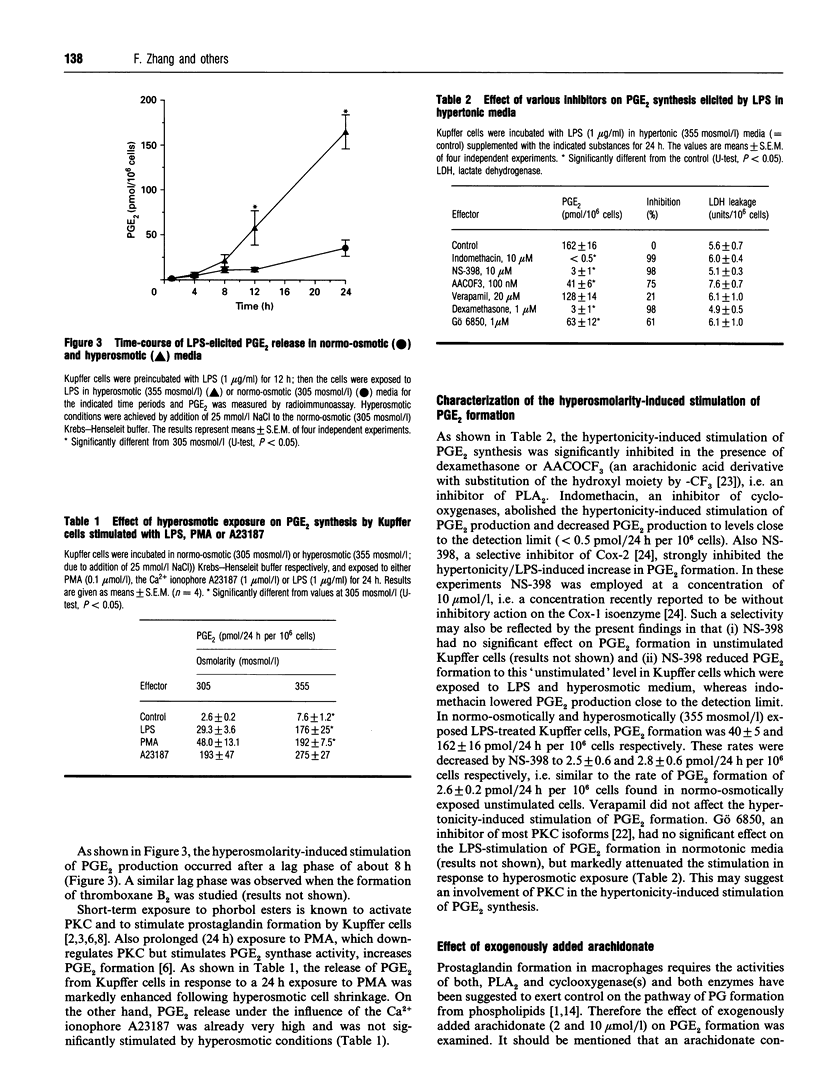
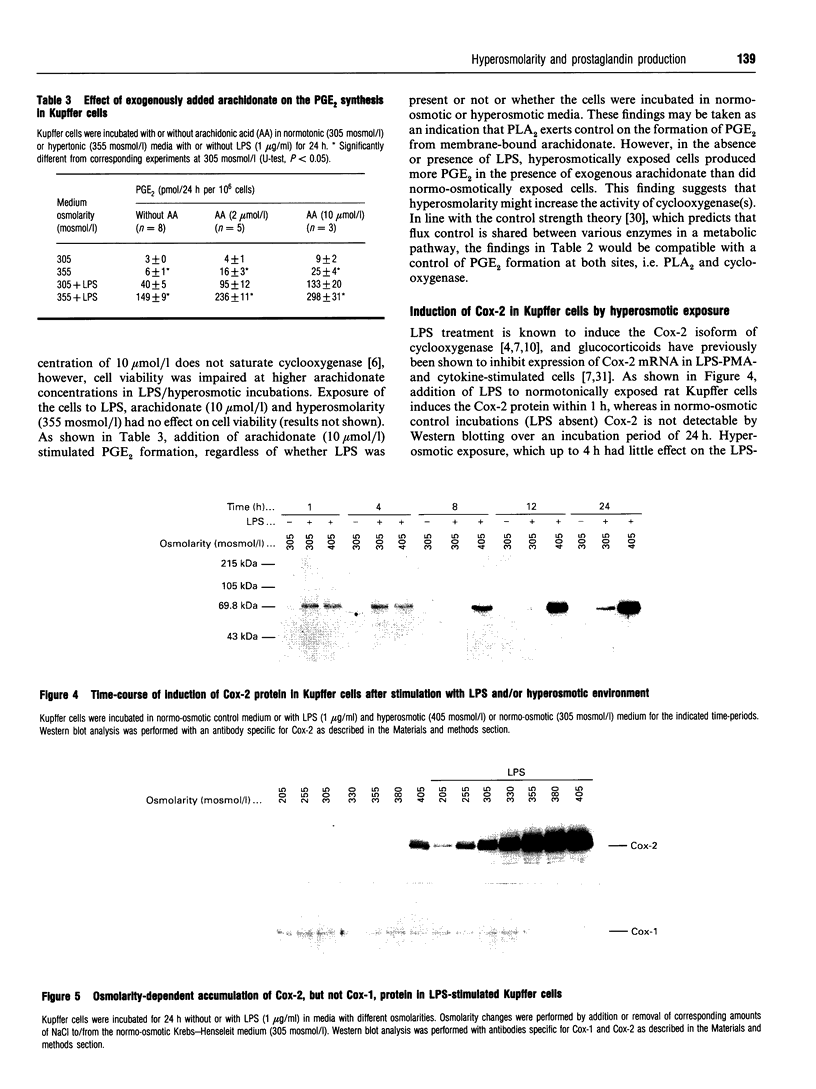
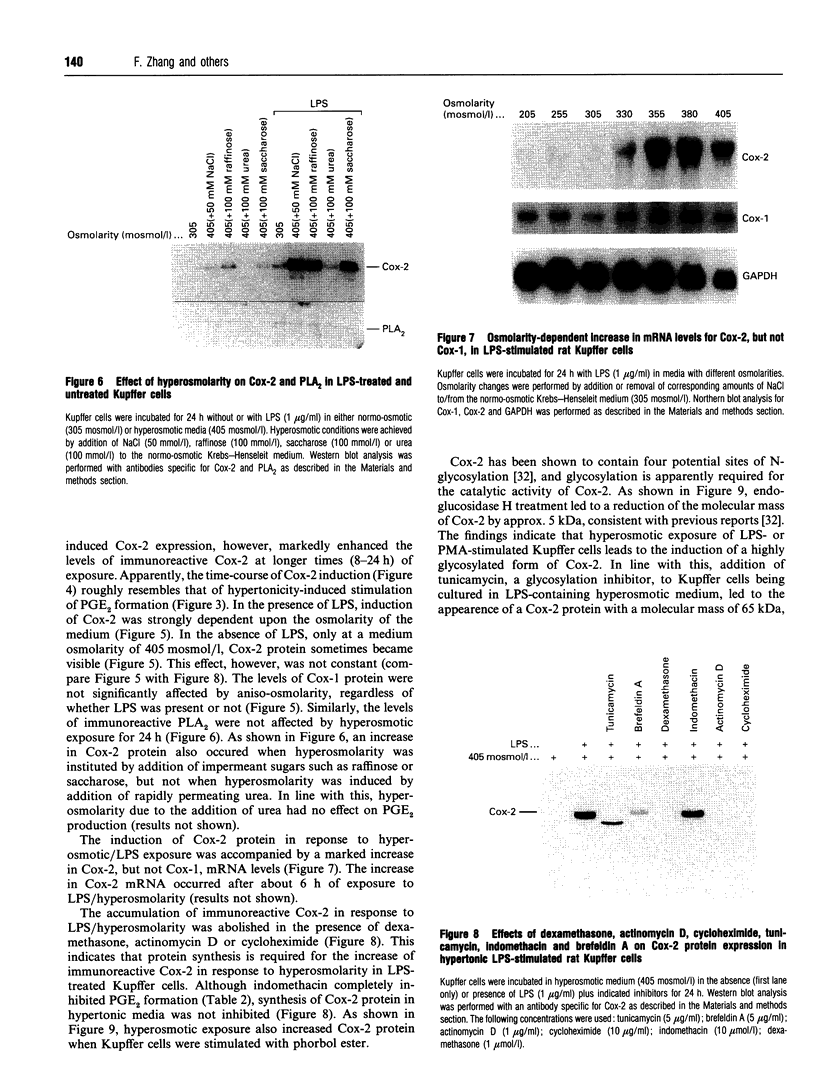
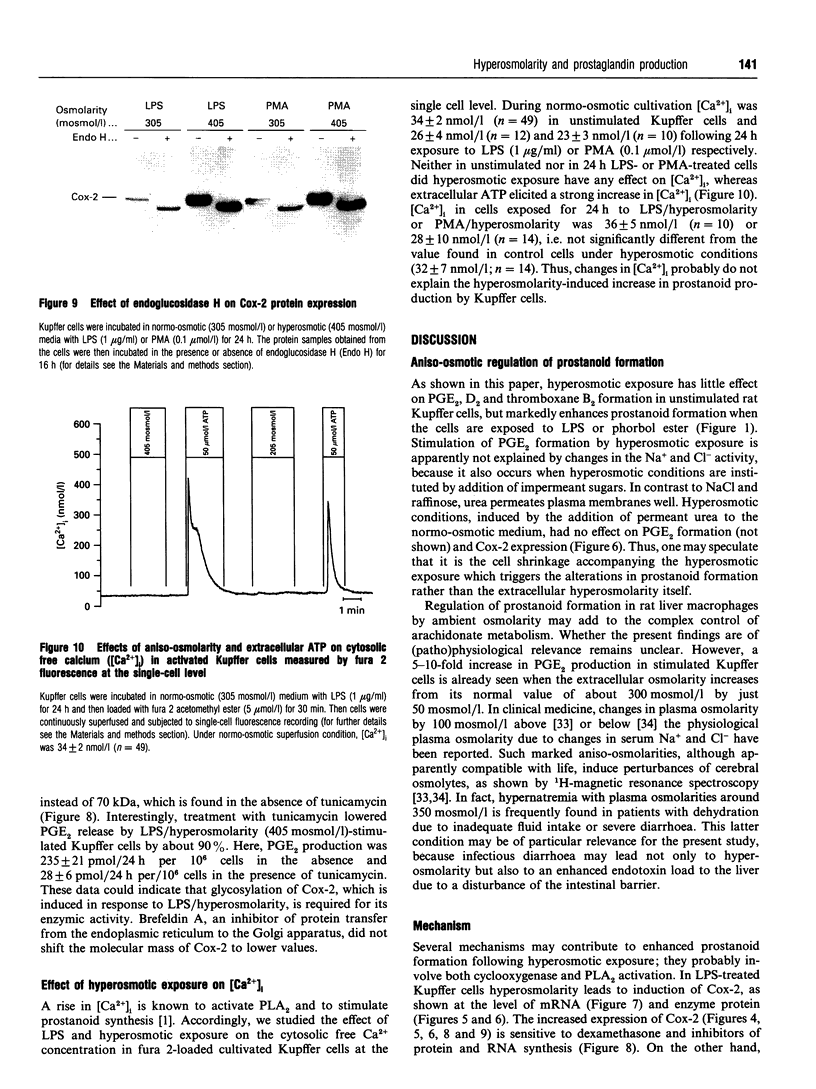
The effect of aniso-osmotic exposure on the level of inducible cyclooxygenase (Cox-2) and on prostanoid synthesis was studied in cultured rat liver macrophages (Kupffer cells). In lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-stimulated Kupffer cells, hyperosmotic (355 mosmol/l) exposure, due to addition of NaCl or impermeant sugars, markedly increased prostaglandin (PG) E2, D2 and thromboxane B2 synthesis in a time- and osmolarity-dependent manner. Increased prostanoid production was observed about 8 h after exposure to LPS in hyperosmotic medium compared to Kupffer cells treated with LPS under normotonic (305 mosmol/l) conditions. A similar stimulatory effect of hyperosmolarity on PGE2 production was also seen when arachidonate was added exogenously. Hyperosmotic stimulation of PGE2 production was accompanied by a strong induction of Cox-2 mRNA levels and an increase in immunoreactive Cox-2, whereas the levels of immunoreactive phospholipase A2 and cyclooxygenase-1 did not change significantly. Dexamethasone, indomethacin and the selective Cox-2 inhibitor, NS-398, abolished the hypertonicity-induced stimulation of PGE2 formation; dexamethasone also prevented the increase in Cox-2 mRNA and protein. The increase of immunoreactive Cox-2 lasted for about 24 h and was also blocked by actinomycin D or cycloheximide, but not by brefeldin A. Tunicamycin or treatment with endoglucosidase H reduced the molecular mass of hypertonicity-induced Cox-2 by 5 kDa. Tunicamycin treatment also suppressed the hypertonicity-induced stimulation of PGE2 production. The hyperosmolarity/LPS-induced stimulation of prostaglandin formation was partly sensitive to protein kinase C inhibition but was not accompanied by an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration. The data suggest that osmolarity may be a critical factor in the regulation of Cox-2 expression and prostanoid production in activated rat liver macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Sagi D., Suhan J. P., McCormick F., Feramisco J. R. Localization of phospholipase A2 in normal and ras-transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1649–1658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. R., Ferris D. K., Colburn N. H., Sobel M. E. A family of mitogen-activated protein kinase-related proteins interacts in vivo with activator protein-1 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9401–9404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster J. L., de Valoir T., Dwyer N. D., Winter E., Gustin M. C. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in yeast. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1760–1763. doi: 10.1126/science.7681220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channon J. Y., Leslie C. C. A calcium-dependent mechanism for associating a soluble arachidonoyl-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 with membrane in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5409–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W., Liu H., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Platelet-activating factor-stimulated protein tyrosine phosphorylation and eicosanoid synthesis in rat Kupffer cells. Evidence for calcium-dependent and protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6725–6735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofford L. J., Wilder R. L., Ristimäki A. P., Sano H., Remmers E. F., Epps H. R., Hla T. Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 expression in rheumatoid synovial tissues. Effects of interleukin-1 beta, phorbol ester, and corticosteroids. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1095–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI117060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt D. L. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase: regulation of enzyme expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 8;1083(2):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90032-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K. Biologically active products of stimulated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):245–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieter P., Schulze-Specking A., Karck U., Decker K. Prostaglandin release but not superoxide production by rat Kupffer cells stimulated in vitro depends on Na+/H+ exchange. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):201–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyster J., Hidaka H., Decker K., Dieter P. Proteinkinase C beta-isoform triggers the formation of prostanoids and superoxide in liver macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):1247–1253. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyhorn S., Schlayer H. J., Henninger H. P., Dieter P., Hermann R., Woort-Menker M., Becker H., Schaefer H. E., Decker K. Rat hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells in monolayer culture. Biochemical and ultrastructural characteristics. J Hepatol. 1988 Feb;6(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkenzeller G., Newsome W., Lang F., Häussinger D. Increase of c-jun mRNA upon hypo-osmotic cell swelling of rat hepatoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 7;340(3):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. R. Eicosanoids. Critical agents in the physiological process and cellular injury. Arch Surg. 1993 Nov;128(11):1192–1196. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420230020003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futaki N., Takahashi S., Yokoyama M., Arai I., Higuchi S., Otomo S. NS-398, a new anti-inflammatory agent, selectively inhibits prostaglandin G/H synthase/cyclooxygenase (COX-2) activity in vitro. Prostaglandins. 1994 Jan;47(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galcheva-Gargova Z., Dérijard B., Wu I. H., Davis R. J. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):806–808. doi: 10.1126/science.8047888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser K. B., Sung A., Bauer J., Weichman B. M. Regulation of eicosanoid biosynthesis in the macrophage. Involvement of protein tyrosine phosphorylation and modulation by selective protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 9;45(3):711–721. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90147-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewe M., Duyster J., Dieter P., Henninger H., Schulze-Specking A., Decker K. Prostaglandin D2 and E2 syntheses in rat Kupffer cells are antagonistically regulated by lipopolysaccharide and phorbol ester. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1992 Aug;373(8):655–664. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Identification and characterization of a hormonally regulated form of phospholipase A2 in rat renal mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16645–16651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib A., Créminon C., Frobert Y., Grassi J., Pradelles P., Maclouf J. Demonstration of an inducible cyclooxygenase in human endothelial cells using antibodies raised against the carboxyl-terminal region of the cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23448–23454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel S. L., Monick M. M., Hunninghake G. W. Lipopolysaccharide induces prostaglandin H synthase-2 protein and mRNA in human alveolar macrophages and blood monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):391–396. doi: 10.1172/JCI116971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett J. A., Roth R. A. Hepatic and extrahepatic pathobiology of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Pharmacol Rev. 1993 Dec;45(4):382–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Lang F., Gerok W. Regulation of cell function by the cellular hydration state. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):E343–E355. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.3.E343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Laubenberger J., vom Dahl S., Ernst T., Bayer S., Langer M., Gerok W., Hennig J. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies on human brain myo-inositol in hypo-osmolarity and hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1475–1480. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90552-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Arcinue E., Ross B. D. Brief report: organic osmolytes in the brain of an infant with hypernatremia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 18;331(7):439–442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408183310704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Soyoola E., Chanmugam P., Hart S., Sun W., Zhong H., Liou S., Simmons D., Hwang D. Selective expression of mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25934–25938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny-Baron G., Kazanietz M. G., Mischak H., Blumberg P. M., Kochs G., Hug H., Marmé D., Schächtele C. Selective inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by the indolocarbazole Gö 6976. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9194–9197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masferrer J. L., Zweifel B. S., Manning P. T., Hauser S. D., Leahy K. M., Smith W. G., Isakson P. C., Seibert K. Selective inhibition of inducible cyclooxygenase 2 in vivo is antiinflammatory and nonulcerogenic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3228–3232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Turk J., Jakschik B. A., Morrison A. R., Lefkowith J. B. Arachidonic acid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:69–102. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome W. P., Warskulat U., Noe B., Wettstein M., Stoll B., Gerok W., Häussinger D. Modulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA levels by the hepatocellular hydration state. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304(Pt 2):555–560. doi: 10.1042/bj3040555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M. G., Chilton F. H., Huggins E. M., Jr, McCall C. E. Lipopolysaccharide priming of alveolar macrophages for enhanced synthesis of prostanoids involves induction of a novel prostaglandin H synthase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14547–14550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto J. C., DeWitt D. L., Smith W. L. N-glycosylation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthases-1 and -2 and their orientations in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18234–18242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannkuche H. J., Kaever V., Gemsa D., Resch K. Regulation of prostaglandin synthesis by protein kinase C in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):471–478. doi: 10.1042/bj2600471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristimäki A., Garfinkel S., Wessendorf J., Maciag T., Hla T. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by interleukin-1 alpha. Evidence for post-transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11769–11775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen G. D., Birkenmeier T. M., Raz A., Holtzman M. J. Identification of a cyclooxygenase-related gene and its potential role in prostaglandin formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1358–1365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91819-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse J., Cohen P., Trigon S., Morange M., Alonso-Llamazares A., Zamanillo D., Hunt T., Nebreda A. R. A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1027–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R., Häussinger D. Characterization of the swelling-induced alkalinization of endocytotic vesicles in fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran-loaded rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1995 Jul 1;309(Pt 1):19–24. doi: 10.1042/bj3090019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L., Meade E. A., DeWitt D. L. Pharmacology of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase isozymes-1 and -2. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Apr 18;714:136–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb12037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street I. P., Lin H. K., Laliberté F., Ghomashchi F., Wang Z., Perrier H., Tremblay N. M., Huang Z., Weech P. K., Gelb M. H. Slow- and tight-binding inhibitors of the 85-kDa human phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 15;32(23):5935–5940. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]