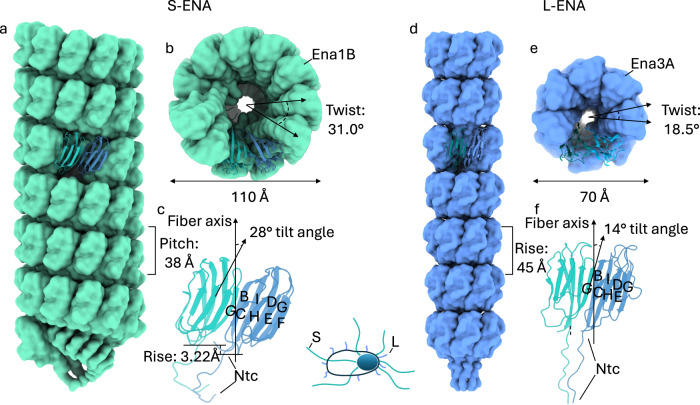
Fig. 3. Structural comparison between the S- and L-ENA fiber architectures.
a Side and b on-axis view of an S-ENA fiber (pdb-id: 7A02) composed of Ena1B subunits. Helical parameters: Rise: 3.22 Å, Twist: 31.0°, Pitch: 38 Å, c Dimeric contacts of Ena1B subunits via β-sheet augmentation at the interface between the G and C strands. Subunits are tilted 28° with respect to the fiber axis. This out-of-plane interaction leads to a helical stacking of Ena1B monomers, d Side and e on-axis view of an L-ENA fiber (pdb-id: 8PDZ) composed of Ena3A subunits. Helical parameters: Rise = pitch: 45 Å, Twist: 18.5°, f Dimeric contacts of Ena3A subunits via β-sheet augmentation at the interface between the G and C strands. Although subunits are tilted 14° with respect to the fiber axis, their contacts remain in-plane yielding a heptameric ring.