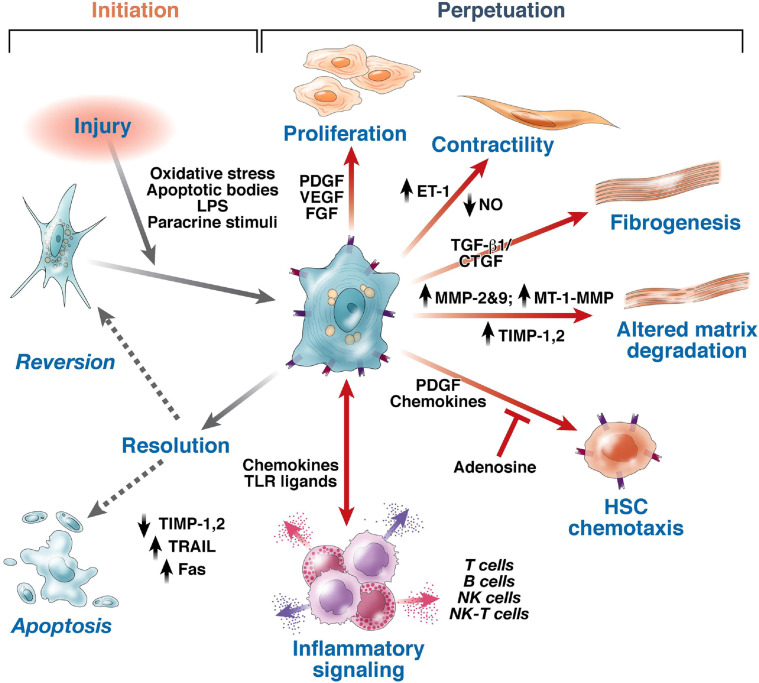
Figure 8.
Pathways of hepatic stellate cell activation[139]. Features of stellate cell activation can be distinguished between those that stimulate initiation and those that contribute to perpetuation. Initiation is provoked by soluble stimuli that include oxidant stress signals (reactive oxygen intermediates), apoptotic bodies, lipopolysaccharide, and paracrine stimuli from neighboring cell types including hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cells), sinusoidal endothelium, and hepatocytes. Perpetuation follows, characterized by a number of specific phenotypic changes including proliferation, contractility, fibrogenesis, altered matrix degradation, chemotaxis, and inflammatory signaling. FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; ET-1: Endothelin-1; NK: Natural killer; NO: Nitric oxide; MT: Membrane type. Citation: Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008; 134: 1655-1669. Copyright © AGA Institute 2008. Published by Elsevier Inc.