Abstract
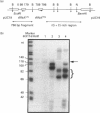
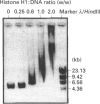
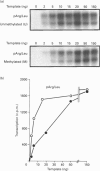
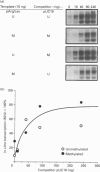
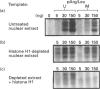
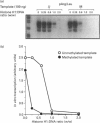
We have previously shown that DNA methylation acts as a focus for the formation of inactive chromatin in vivo. We have investigated the mechanism further by in vitro transcription of a template containing two tRNA genes and an extensive (G+C)-rich sequence characteristic of a CpG island. The extent of transcription from the unmethylated or fully methylated template was assayed in the presence of varied levels of histone H1. The transcriptional activity of both templates was inhibited by increasing amounts of histone H1, although inhibition with the methylated template occurs at a lower H1:DNA ratio. The H1c variant shows the greatest preferential inhibition of the methylated template. We demonstrated that histone H1 complexed to DNA is one of the factors that inhibits transcription by preventing the formation of initiation complexes, particularly on methylated template, rather than the formation of disordered H1.DNA aggregates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L. DNA methylation. The effect of minor bases on DNA-protein interactions. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):309–320. doi: 10.1042/bj2650309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antequera F., Macleod D., Bird A. P. Specific protection of methylated CpGs in mammalian nuclei. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball D. J., Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. 5-methylcytosine is localized in nucleosomes that contain histone H1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5490–5494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser D., Götz F., Schulze-Forster K., Wagner H., Kröger H., Simon D. DNA methylation inhibits transcription by RNA polymerase III of a tRNA gene, but not of a 5S rRNA gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81193-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90526-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Bustin M., Marsaud V., Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. The transcriptionally-active MMTV promoter is depleted of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):273–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caiafa P., Reale A., Allegra P., Rispoli M., D'Erme M., Strom R. Histones and DNA methylation in mammalian chromatin. Differential inhibition by histone H1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 27;1090(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90034-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Kimura T. Electrostatic mechanism of chromatin folding. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):883–896. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90081-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Thomas J. O. Differences in the binding of H1 variants to DNA. Cooperativity and linker-length related distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 1;178(1):225–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Thomas J. O. Salt-dependent co-operative interaction of histone H1 with linear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Goodman H. M. CpG methylation inhibits proenkephalin gene expression and binding of the transcription factor AP-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3975–3982. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Ehrlich K. C. Effect of DNA methylation on the binding of vertebrate and plant proteins to DNA. EXS. 1993;64:145–168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9118-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. D. Structure of the 30 nm chromatin fiber. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):375–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrard W. T. Histone H1 and the conformation of transcriptionally active chromatin. Bioessays. 1991 Feb;13(2):87–88. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessmann A. DNA methylation, chromatin structure and the regulation of gene expression. EXS. 1993;64:404–424. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9118-9_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano V., Gerchman S. E., Schneider D. K., Ramakrishnan V. Histone H1 is located in the interior of the chromatin 30-nm filament. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):351–354. doi: 10.1038/368351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Functional steps in transcription initiation and reinitiation from the major late promoter in a HeLa nuclear extract. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3452–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hergersberg M. Biological aspects of cytosine methylation in eukaryotic cells. Experientia. 1991 Dec 1;47(11-12):1171–1185. doi: 10.1007/BF01918381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higurashi M., Cole R. D. The combination of DNA methylation and H1 histone binding inhibits the action of a restriction nuclease on plasmid DNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8619–8625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Schaffner W. CpG methylation of the cAMP-responsive enhancer/promoter sequence TGACGTCA abolishes specific factor binding as well as transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):612–619. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Hofsteenge J. The repressor MDBP-2 is a member of the histone H1 family that binds preferentially in vitro and in vivo to methylated nonspecific DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9499–9503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Saluz H. P., Pawlak A. Estradiol down regulates the binding activity of an avian vitellogenin gene repressor (MDBP-2) and triggers a gradual demethylation of the mCpG pair of its DNA binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5771–5775. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure of transcriptionally competent and repressed genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3997–4006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S. U., Goddard J. P., Adams R. L. Inactive chromatin spreads from a focus of methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7372–7379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Childs G. Characterization of the structure and transcriptional patterns of the gene encoding the late histone subtype H1-beta of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1842–1844. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A., Yeivin A., Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y., Razin A. Histone H1-mediated inhibition of transcription initiation of methylated templates in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21754–21759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. D., Meehan R. R., Henzel W. J., Maurer-Fogy I., Jeppesen P., Klein F., Bird A. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90610-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louters L., Chalkley R. Exchange of histones H1, H2A, and H2B in vivo. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3080–3085. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
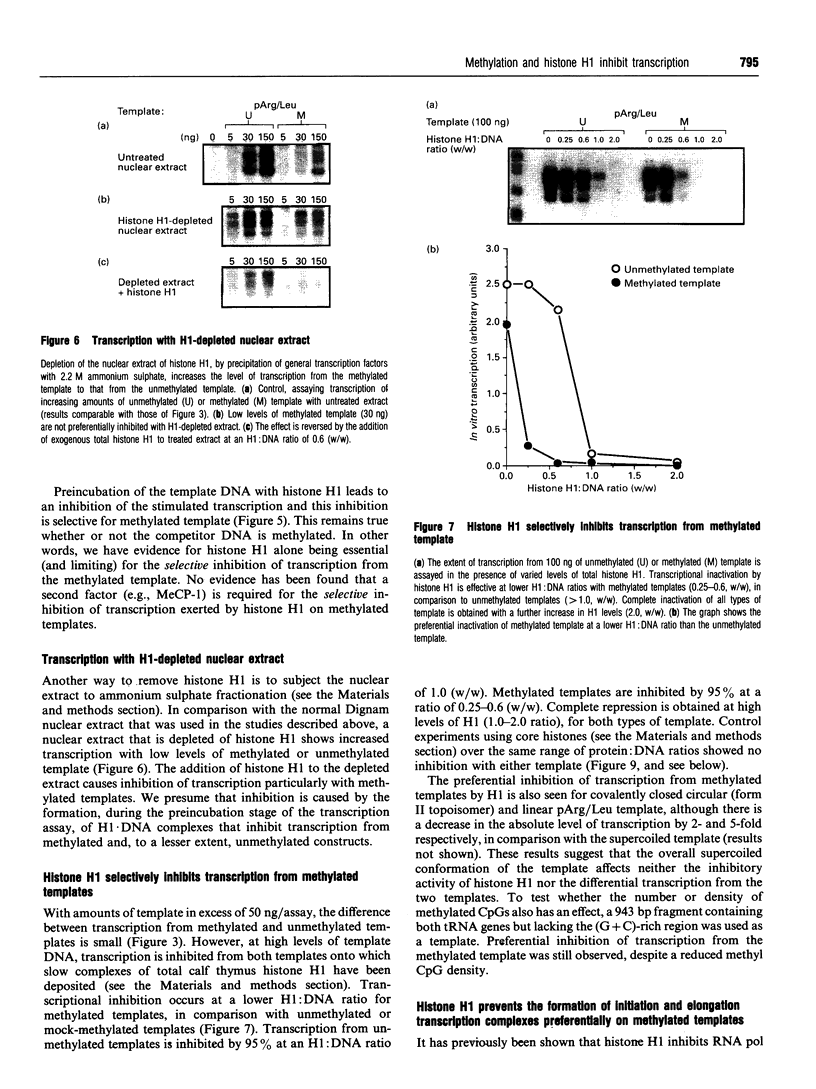
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., McKay S., Kleiner E. L., Bird A. P. Identification of a mammalian protein that binds specifically to DNA containing methylated CpGs. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesada P., Farina B., Jones R. Poly(ADP-ribosylation) of nuclear proteins in rat testis correlates with active spermatogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 1;1007(2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene expression. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):451–458. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.451-458.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Campos A., Shimamura A., Worcel A. Assembly and properties of chromatin containing histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):135–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro R., D'Erme M., Mastrantonio S., Reale A., Marenzi S., Saluz H. P., Strom R., Caiafa P. Binding of histone H1e-c variants to CpG-rich DNA correlates with the inhibitory effect on enzymic DNA methylation. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 1;305(Pt 3):739–744. doi: 10.1042/bj3050739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Sapp M., Rodriguez-Campos A., Worcel A. Histone H1 represses transcription from minichromosomes assembled in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5573–5584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Khabaza A. J. Cross-linking of histone H1 in chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):501–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Histone-H1-dependent chromatin superstructures and the suppression of gene activity. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90522-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Dominant and specific repression of Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA genes and satellite I DNA by histone H1. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):527–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Asiedu C. K., Supakar P. C., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Binding sites in mammalian genes and viral gene regulatory regions recognized by methylated DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6253–6260. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]