Abstract
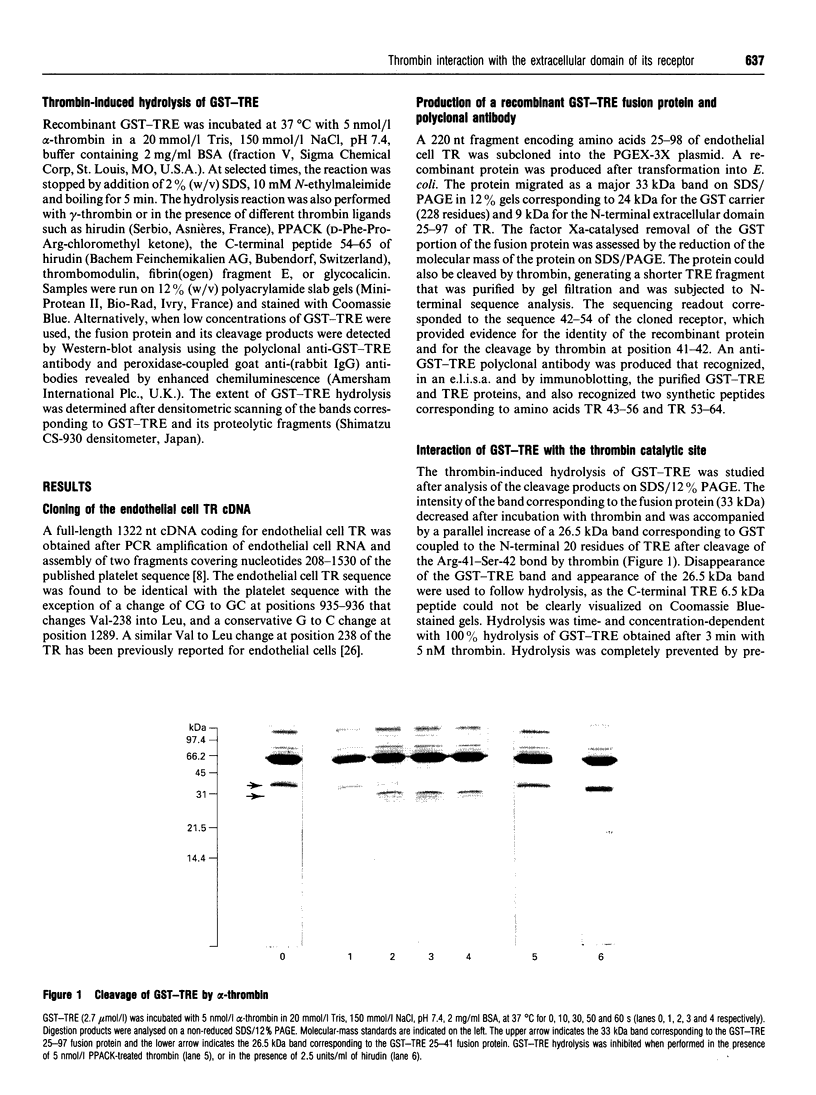
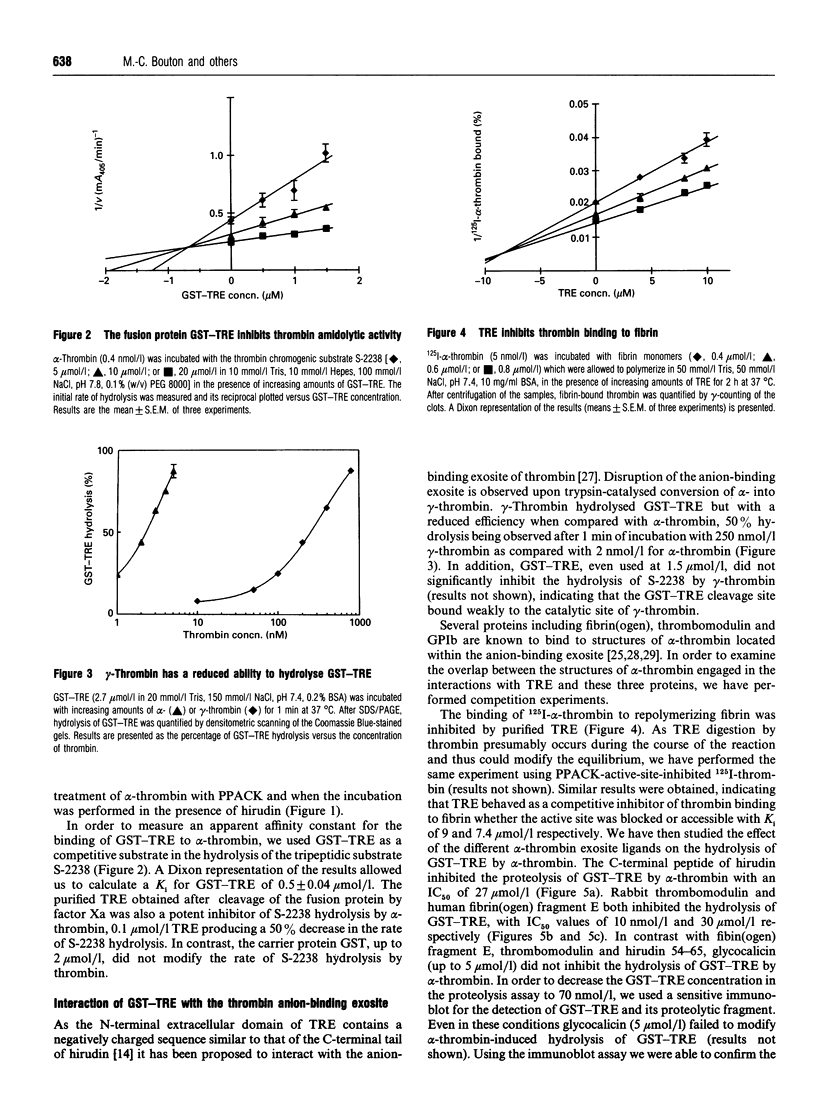
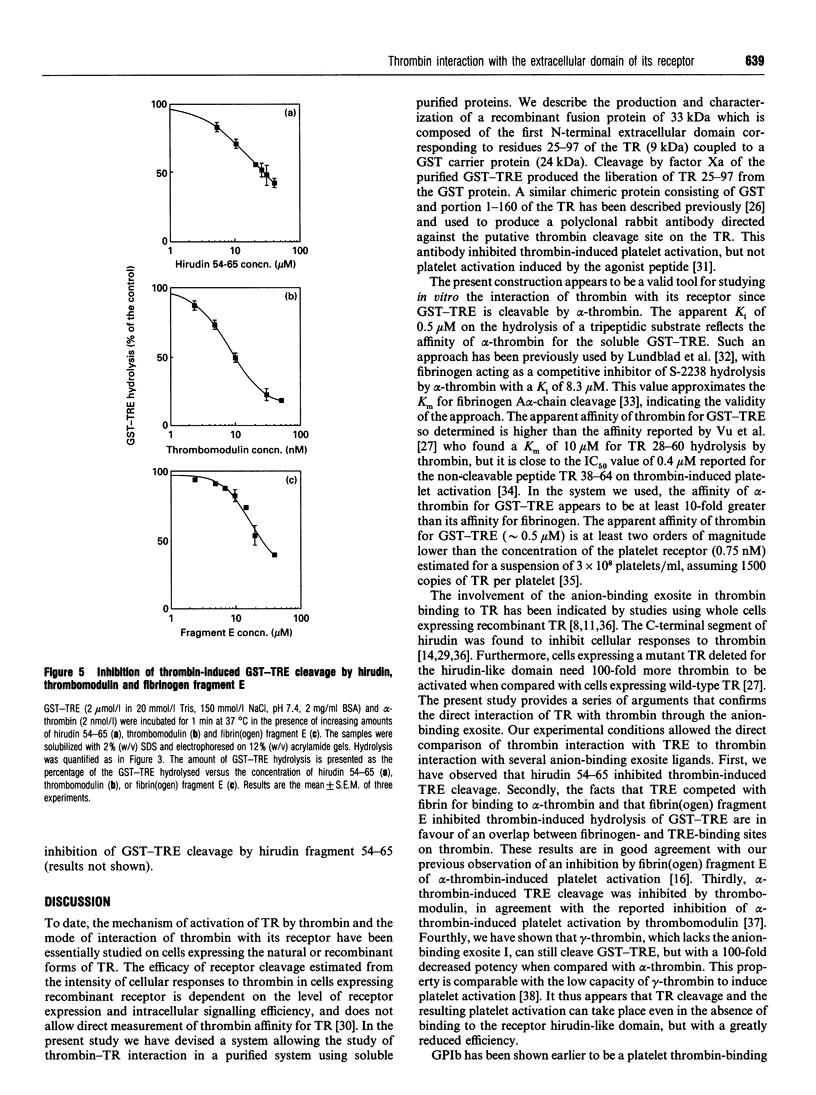
The cDNA of the human endothelial cell thrombin receptor has been cloned and a chimeric fusion protein consisting of glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and the portion 25-97 corresponding to the N-terminal first extracellular domain of the thrombin receptor (TRE) has been expressed in Escherichia coli. Introduction of a factor Xa cleavage site in the fusion protein allowed purification of TRE after removal from the GST carrier protein. Purified GST-TRE or TRE have been tested in solution for their ability to interact with thrombin. alpha-Thrombin cleaved the fusion protein at position Arg-41-Ser-42 of TRE in a time- and concentration-dependent manner and GST-TRE competed with the tripeptidic substrate S-2238 for hydrolysis by thrombin (Ki = 0.5 microM). gamma-Thrombin that lacks the anion-binding exosite was 100-fold less potent than alpha-thrombin at cleaving GST-TRE. TRE competed with polymerizing fibrin monomers for binding to thrombin (Ki = 7.5 microM). The cleavage of GST-TRE by alpha-thrombin was inhibited by several alpha-thrombin exosite ligands such as the C-terminal peptide of hirudin, thrombomodulin and fibrin(ogen) fragment E. In contrast, platelet glycocalicin did not inhibit GST-TRE cleavage. In conclusion, the use of purified soluble GST-TRE allowed us to derive an affinity constant for thrombin interaction with the N-terminal domain of the receptor and to confirm the location of the cleavage site at Arg41-Ser-42 of the receptor. The importance of the thrombin anion-binding exosite for thrombin receptor recognition is highlighted by the low reactivity of gamma-thrombin for GST-TRE and by competition experiments, which in addition indicate that binding sites for fibrin(ogen), thrombomodulin and GST-TRE are overlapping. In contrast, binding of thrombin to GST-TRE and glycocalicin are not mutually exclusive, indicating that glycocalicin and TRE interact with discrete subsites within the large groove that constitutes the anion-binding exosite.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahou W. F., Coller B. S., Potter C. L., Norton K. J., Kutok J. L., Goligorsky M. S. The thrombin receptor extracellular domain contains sites crucial for peptide ligand-induced activation. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1405–1413. doi: 10.1172/JCI116344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartha K., Brisson C., Archipoff G., de la Salle C., Lanza F., Cazenave J. P., Beretz A. Thrombin regulates tissue factor and thrombomodulin mRNA levels and activities in human saphenous vein endothelial cells by distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):421–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezeaud A., Denninger M. H., Guillin M. C. Interaction of human alpha-thrombin and gamma-thrombin with antithrombin III, protein C and thrombomodulin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):491–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Turk D., Karshikov A. The refined 1.9-A X-ray crystal structure of D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone-inhibited human alpha-thrombin: structure analysis, overall structure, electrostatic properties, detailed active-site geometry, and structure-function relationships. Protein Sci. 1992 Apr;1(4):426–471. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouton M. C., Jandrot-Perrus M., Bezeaud A., Guillin M. C. Late-fibrin(ogen) fragment E modulates human alpha-thrombin specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jul 1;215(1):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Vassallo R. R., Jr, Belmonte E., Ahuja M., Cichowski K., Hoxie J. A. Structure and function of the human platelet thrombin receptor. Studies using monoclonal antibodies directed against a defined domain within the receptor N terminus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13795–13798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Levin R. I., Garry K. Human neutrophil elastase modulates platelet function by limited proteolysis of membrane glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):657–666. doi: 10.1172/JCI111744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I. Characterization of a functional thrombin receptor. Issues and opportunities. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):351–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI115592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzucato M., Masotti A., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Ruggeri Z. M. Function of glycoprotein Ib alpha in platelet activation induced by alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23776–23783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler T. C. Hypothetical models for the thrombin-platelet interaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:67–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Carroll R. C., Esmon C. T. Thrombomodulin blocks the ability of thrombin to activate platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12238–12242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Regulation of thrombin generation and functions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1988 Jul;14(3):234–240. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Wiesel M. L., Grunebaum L., Pereillo J. M., Gauchy J., Schuhler S., Freund G., Cazenave J. P. Activation of human protein C by blood coagulation factor Xa in the presence of anionic phospholipids. Enhancement by sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):341–348. doi: 10.1042/bj2610341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly P., Gould N. L. Thrombin receptors of human platelets: thrombin binding and antithrombin properties of glycoprotein I. Br J Haematol. 1979 May;42(1):137–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronke R. S., Bergman B. L., Baker J. B. Thrombin interaction with platelets. Influence of a platelet protease nexin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3030–3036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. T., Jamieson G. A. Platelet activation by thrombin in the absence of the high-affinity thrombin receptor. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2151–2157. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. T., Jamieson G. A. The glycocalicin portion of platelet glycoprotein Ib expresses both high and moderate affinity receptor sites for thrombin. A soluble radioreceptor assay for the interaction of thrombin with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13224–13229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess D., Schaller J., Rickli E. E., Clemetson K. J. Identification of the disulphide bonds in human platelet glycocalicin. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Lewis S. D., Shafer J. A. Steady state kinetic parameters for the thrombin-catalyzed conversion of human fibrinogen to fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9276–9282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Charo I. F., Nelken N. A., Esmon N., Esmon C. T., Coughlin S. R. "Mirror image" antagonists of thrombin-induced platelet activation based on thrombin receptor structure. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):444–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI115604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Ishii K., Coughlin S. R. Cloned platelet thrombin receptor is necessary for thrombin-induced platelet activation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1350–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Chen J., Ishii M., Koch W. J., Freedman N. J., Lefkowitz R. J., Coughlin S. R. Inhibition of thrombin receptor signaling by a G-protein coupled receptor kinase. Functional specificity among G-protein coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1125–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. A., Okumura T. Reduced thrombin binding and aggregation in Bernard-Soulier platelets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):861–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI109000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandrot-Perrus M., Clemetson K. J., Huisse M. G., Guillin M. C. Thrombin interaction with platelet glycoprotein Ib: effect of glycocalicin on thrombin specificity. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2781–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandrot-Perrus M., Didry D., Guillin M. C., Nurden A. T. Cross-linking of alpha and gamma-thrombin to distinct binding sites on human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 1;174(2):359–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandrot-Perrus M., Guillin M. C., Nurden A. T. Human gamma-thrombin: lack of correlation between a platelet functional response and glycoprotein V hydrolysis. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Oct 28;58(3):915–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandrot-Perrus M., Huisse M. G., Krstenansky J. L., Bezeaud A., Guillin M. C. Effect of the hirudin carboxy-terminal peptide 54-65 on the interaction of thrombin with platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Sep 2;66(3):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandrot-Perrus M., Rendu F., Caen J. P., Levy-Toledano S., Guillin M. C. The common pathway for alpha- and gamma-thrombin-induced platelet activation is independent of GPIb: a study of Bernard-Soulier platelets. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jul;75(3):385–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb04353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bonniec B. F., Esmon C. T. Glu-192----Gln substitution in thrombin mimics the catalytic switch induced by thrombomodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7371–7375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Nesheim M. E., Straight D. L., Sailor S., Bowie J., Jenzano J. W., Roberts J. D., Mann K. G. Bovine alpha- and beta-thrombin. Reduced fibrinogen-clotting activity of beta-thrombin is not a consequence of reduced affinity for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6991–6995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurov A. V., Vinogradov D. V., Vlasik T. N., Repin V. S., Booth W. J., Berndt M. C. Characterization of an antiglycoprotein Ib monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits platelet-thrombin interaction. Thromb Res. 1991 Jun 15;62(6):673–684. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney M. M., Parkinson A. A simple, non-chromatographic procedure to purify immunoglobulins from serum and ascites fluid. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Feb 11;96(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Vaheri A., Choate J. J., Gahmberg C. G. Action of thrombin on surface glycoproteins of human platelets. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):437–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naski M. C., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Maraganore J. M., Olson S. T., Shafer J. A. The COOH-terminal domain of hirudin. An exosite-directed competitive inhibitor of the action of alpha-thrombin on fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13484–13489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngaiza J. R., Manley G., Grulich-Henn J., Krstenansky J. L., Jaffe E. A. The fibrinogen anion-binding exosite of thrombin is necessary for induction of rises in intracellular calcium and prostacyclin production in endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Apr;151(1):190–196. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton K. J., Scarborough R. M., Kutok J. L., Escobedo M. A., Nannizzi L., Coller B. S. Immunologic analysis of the cloned platelet thrombin receptor activation mechanism: evidence supporting receptor cleavage, release of the N-terminal peptide, and insertion of the tethered ligand into a protected environment. Blood. 1993 Oct 1;82(7):2125–2136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura T., Hasitz M., Jamieson G. A. Platelet glycocalicin. Interaction with thrombin and role as thrombin receptor of the platelet surface. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3435–3443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen U. B., Vouret-Craviari V., Jallat S., Schlesinger Y., Pagès G., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Pouysségur J., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. cDNA cloning and expression of a hamster alpha-thrombin receptor coupled to Ca2+ mobilization. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Detwiler T. C. Platelet thrombin receptors. Binding of alpha-thrombin is coupled to signal generation by a chymotrypsin-sensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6626–6632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Lentz S. R., Dittman W. A., Wen D., Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to recombinant human thrombomodulin: effect of hirudin, fibrinogen, factor Va, and peptide analogues. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10602–10612. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Hung D. T., Charo I., Coughlin S. R. Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):674–677. doi: 10.1038/353674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicki A. N., Clemetson K. J. Structure and function of platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and V. Effects of leukocyte elastase and other proteases on platelets response to von Willebrand factor and thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye J., Liu L. W., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. The fifth and sixth growth factor-like domains of thrombomodulin bind to the anion-binding exosite of thrombin and alter its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11023–11028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong C., Hayzer D. J., Corson M. A., Runge M. S. Molecular cloning of the rat vascular smooth muscle thrombin receptor. Evidence for in vitro regulation by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16975–16979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



