FIGURE 1.
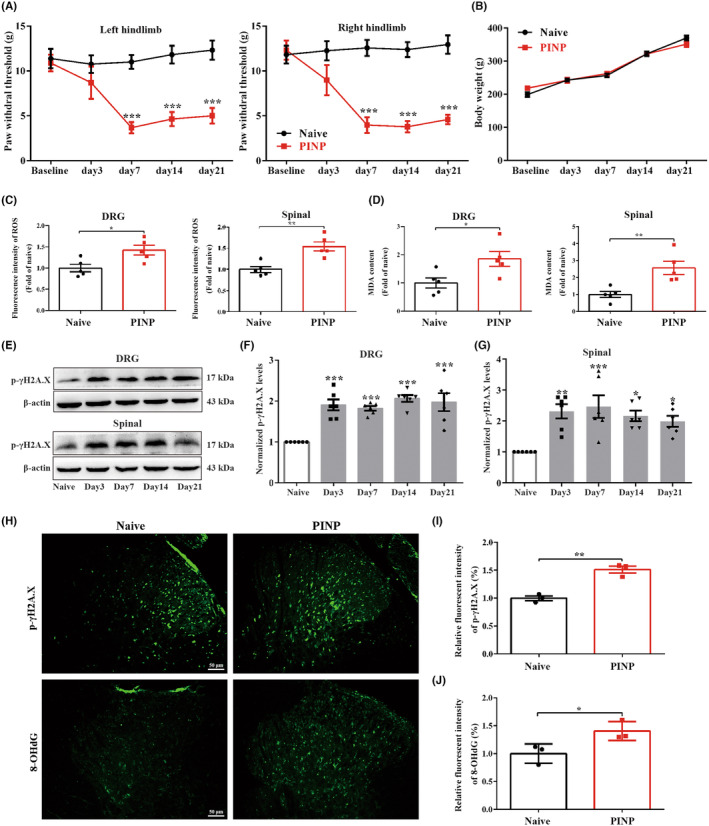
Intraperitoneal administration of paclitaxel results in mechanical allodynia as well as DNA oxidative damage in rats. (A) Paclitaxel injection induced a remarkable reduction in PWTs on the bilateral hindlimbs. Two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, ***p < 0.001 versus Naïve group, n = 8 per group. (B) The body weight showed no remarkable differences in the Naïve and PINP groups. Two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, p > 0.05, n = 8 per group. (C, D) Paclitaxel injection resulted in the upregulation of ROS and MDA levels in the DRGs and spinal cord. Normalized to Naïve group. Unpaired Student's t‐test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus Naïve group, n = 5 per group. (E–G) The levels of p‐γH2A.X (Ser 139) were increased in the DRGs and spinal cord in the PINP group. One‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus Naïve group, n = 6 per group. (H–J) Relative immunofluorescence staining intensities of p‐γH2A.X (Ser 139) and 8‐OHdG in the spinal cord dorsal horn in each group. Normalized to Naïve group. Unpaired Student's t‐test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus Naïve group, n = 3 per group. Scale bar: 50 μm.
