FIGURE 3.
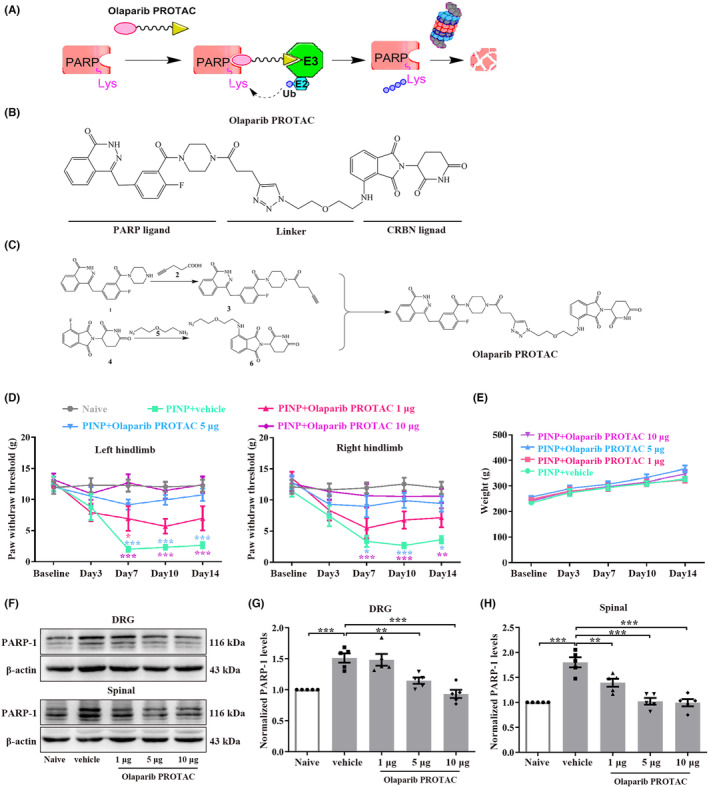
Continuous intrathecal injection of Olaparib PROTAC alleviated paclitaxel injection‐induced mechanical allodynia by inhibition of PARP‐1 in rats. (A) Working model of Olaparib PROTAC. (B) The designed Olaparib PROTAC composed of a PARP ligand, a linker and a CRBN ligand. (C) The details of Olaparib PROTAC synthesis. (D) Repeated intrathecal injection of Olaparib PROTAC (1, 5, or 10 μg/10 μL) reversed the decreased PWTs in a dose‐dependent manner. Two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus PINP+vehicle group, n = 7–8 per group. (E) No significant differences of the body weight were observed in PINP+Olaparib PROTAC groups compared to PINP+vehicle group. Two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, p > 0.05, n = 7 per group. (F–H) Continuous intrathecal injection of Olaparib PROTAC inhibited the upregulations of PARP‐1 protein in the PINP rats in a dose‐dependent manner. One‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus corresponding groups, n = 5 per group.
