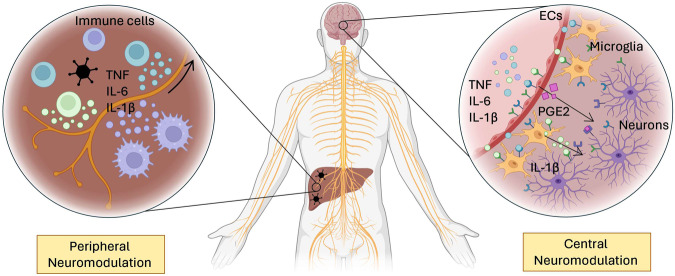
Fig. 2.
Neuromodulation by the immune system. Although the nervous system is immune-privileged, it is not devoid of immunological control. Cytokines impact the central control of metabolism via cellular intermediates. (Left) Peripheral neuromodulation is mediated by neurons of the N. vagus, which are under the direct influence of cytokines produced in the periphery. These signals are sent to the hypothalamus, resulting in central regulation of sickness metabolism. (right) Central neuromodulation occurs directly in the brain. Immunological mediators can cross the endothelial barrier in the hypothalamus and reach microglia. These cells produce cytokines locally, thus amplifying the signal toward neurons. Endothelial cells (ECs) in the hypothalamus also sense cytokines and, in response, produce molecules such as PGE2. This leukotriene is sensed by neurons and mediates metabolic changes such as alterations in body temperature. Made with biorender.com