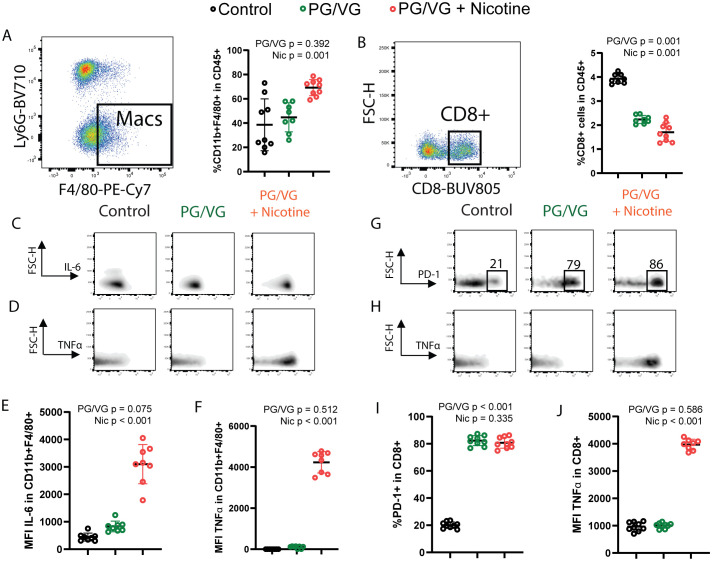
Figure 5.
Whole body exposure of mice e-cigarette aerosol leads to increased myeloid and lymphoid immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. (A) Left, representative flow cytometry pseudocolor dot plot showing gating on lung-infiltrating macrophages from animals exposed to PG/VG with or without 36 mg/ml nicotine as described in Figure 4A . Right, lung-infiltrating macrophage frequency within gated live CD45+ immune cells was not affected by PG/VG (p=0.392; Table 1 ) but increased with the addition of nicotine (p=0.001). (B) Left, representative flow cytometry pseudocolor dot plot showing gating on lung-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. Right, lung-infiltrating CD8+ T cell frequency within gated live CD45+ immune cells fell significantly with exposure to PG/VG (p<0.001; Table 1 ) and about one-third more with the addition of nicotine (p<0.001). (C) Representative flow cytometry density plots showing IL-6 expression in gated lung-infiltrating macrophages. (D) Representative flow cytometry density plots showing TNFα expression in gated lung-infiltrating macrophages. (E) Mean fluorescence intensity of IL-6 in gated lung macrophages was not affected significantly by PG/VG (p=0.075; Table 1 ) but increased significantly with the addition of nicotine (p<0.001). (F) Mean fluorescence intensity of TNFα in gated lung macrophages was not affected significantly by PG/VG (p=0.512; Table 1 ) but increased significantly with the addition of nicotine (p<0.001). (G) Representative flow cytometry density plots showing PD-1 expression in gated lung-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. (H) Representative flow cytometry density plots showing TNFα expression in gated lung- infiltrating CD8+ T cells. (I) Percentage PD-1+ cells in gated lung CD8+ T cells was significantly higher in the presence of PG/VG (p<0.001; Table 1 ) but not affected by addition of nicotine (p=0.335). (J) Mean fluorescence intensity of TNFα in gated lung CD8+ T cells was not significantly different in the presence of PG/VG (p=0.586; Table 1 ) but significantly increased with the addition of nicotine (p<0.001).