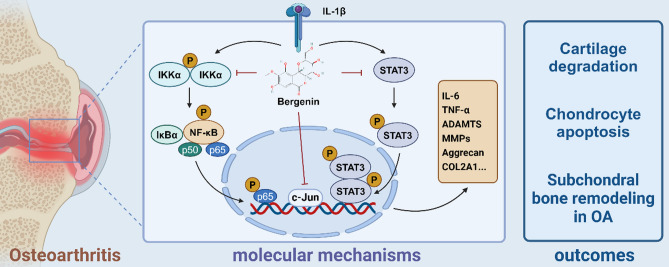
Fig. 8.
Schematic of Ber inhibition of inflammatory pathways in ATDC5 cells in vitro. In general, it inhibits the IL-1β-activated NF-κB, STAT3 signaling pathway as well as subsequent phosphorylation upregulation and phosphorylation into the nucleus and Jun signaling pathway. It ameliorates OA by inhibiting the upregulation of inflammatory factors such as MMPs and ADAMTS and protecting COL2A1 and aggrecan from degradation. Finally, above mechanisms contribute to three outcomes including cartilage degradation, chondrocyte apoptosis and subchondral bone remodeling in OA. Created using biorender.com.