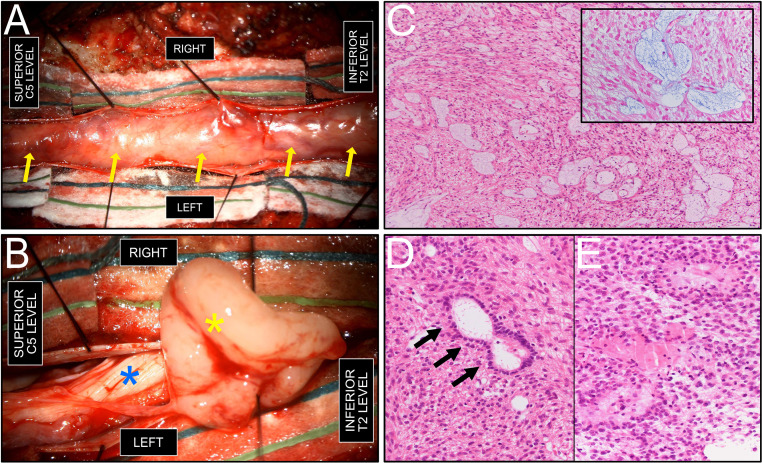
Fig. 2.
Intraoperative and histopathologic findings. (A) intraoperative view, following C5-T2 laminectomy and dural sac opening, showing a tan-colored, well-demarcated encapsulated intradural tumor (arrows), without areas of macroscopic necrosis. (B) Intraoperative view, after partial dissection of the intradural extramedullary mass (yellow asterisk) from the plane of the spinal cord (blue asterisk). (C) Glial epithelial proliferation with focal perivascular myxoid microcysts, typical of myxopapillary ependymoma. Mitotic activity was low. (hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain, 100X original magnification). Inset: Alcian Blue staining highlighting the myxoid content in light blue within microcysts (400X magnification). A strong positivity for GFAP immunohistochemistry was also noted (not shown). (D) ‘True’ ependymal rosette (arrows), consisting of tumor cells arranged around an empty central lumen, characteristic of ‘classic’ spinal ependymoma (H&E stain, 200X magnification). (E) Glial proliferation with tumor cells arranged in perivascular pseudorosettes (H&E stain, 200X magnification).