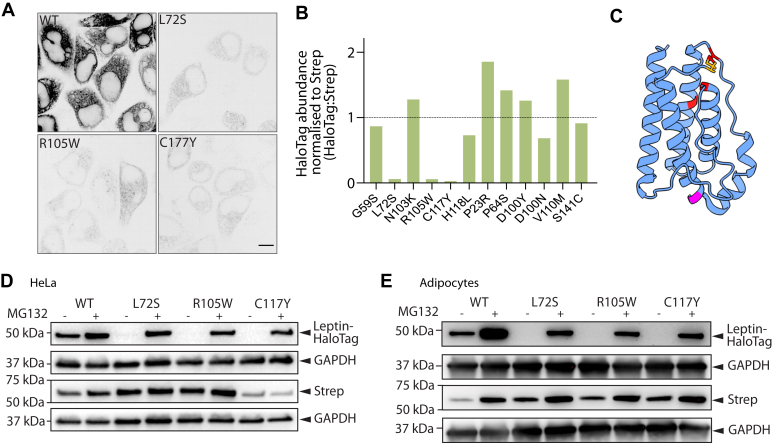
Figure 4.
p.L72S, p.R105W, and p.C117Y leptin variations have low abundance due to proteasomal degradation. A, fluorescence microscographs of HeLa cells expressing WT, p.L72S, p.R105W, and p.C117Y SBP-HaloTag-leptin before biotin addition. Representative of n= 7 for WT SBP-HaloTag-leptin, n = 3 for p.L72S, p.R105W, and p.C117Y SBP-HaloTag-leptin; scale bar: 10 μm. B, quantification of leptin variant protein abundance normalized to Streptavidin-KDEL to account for plasmid integration efficiency and expressed relative to WT protein abundance (black dotted line). Data are n = 2. Error bars = SEM. C, alphaFold-generated model of leptin with signal peptide (amino acids 1–21) removed (44). Positions of variants that cause low leptin expression (L72S, R105W, C117Y) are in red. Position of S141C is in magenta. The position of the disulfide bond between C117 and C167 is in orange. Error bars = SEM. D, HeLa cells expressing WT, p.L2S, p.R105W, or p.C117Y SBP-HaloTag-leptin were treated with 40 μM MG132 for 6 h where indicated, and lysates were analysed by Western blot. Streptavidin abundance was assessed as control for piggybac plasmid genomic insertion efficiency; GAPDH abundance was assessed as loading control. Representative blots of n= 3. Error bars = SEM. E, 3T3-L1 adipocytes expressing WT, p.L2S, p.R105W, or p.C117Y SBP-HaloTag-leptin were treated with 40 μM MG132 for 6 h where indicated, and lysates were analysed by Western blot. Streptavidin abundance was assessed as control for piggybac plasmid genomic insertion efficiency; GAPDH abundance was assessed as a loading control. Representative blots of n = 3.