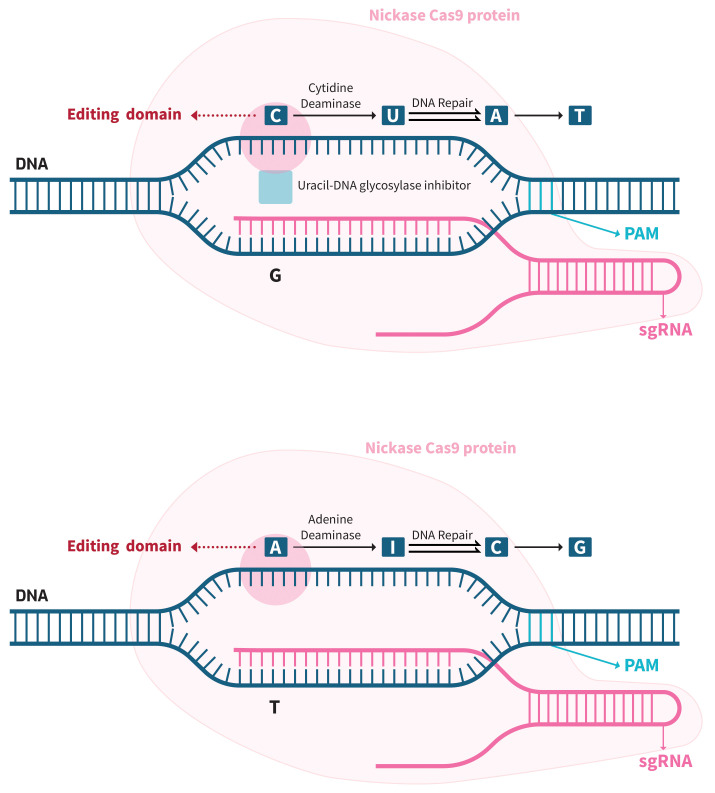
Fig. 1.
CRISPR DNA base-editing tools. A: DNA base-editors have two main components, which are a Cas enzyme for programmable DNA binding and a base modification enzyme for targeted nucleotide change. Two types of DNA base-editors have been developed: cytosine base-editors and adenine base-editors. Cytosine base editing: cytosine deaminase produces uracil, that base pairs as thymidine; uracil-DNA glycosylase inhibitor enhances the efficacy of cytosine base-editing by binding and inhibiting uracil N-glycosylate: adenine base editing: adenine deaminase generates inosine, that base pairs as thymidine (modified from Kantor et al. [18]). PAM, protospacer adjacent motif; sgRNA, small guide RNA; A, adenine; C, cytosine; T, thymine; G, guanine; U, uracil; I, inosine; Cas9, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated protein 9.