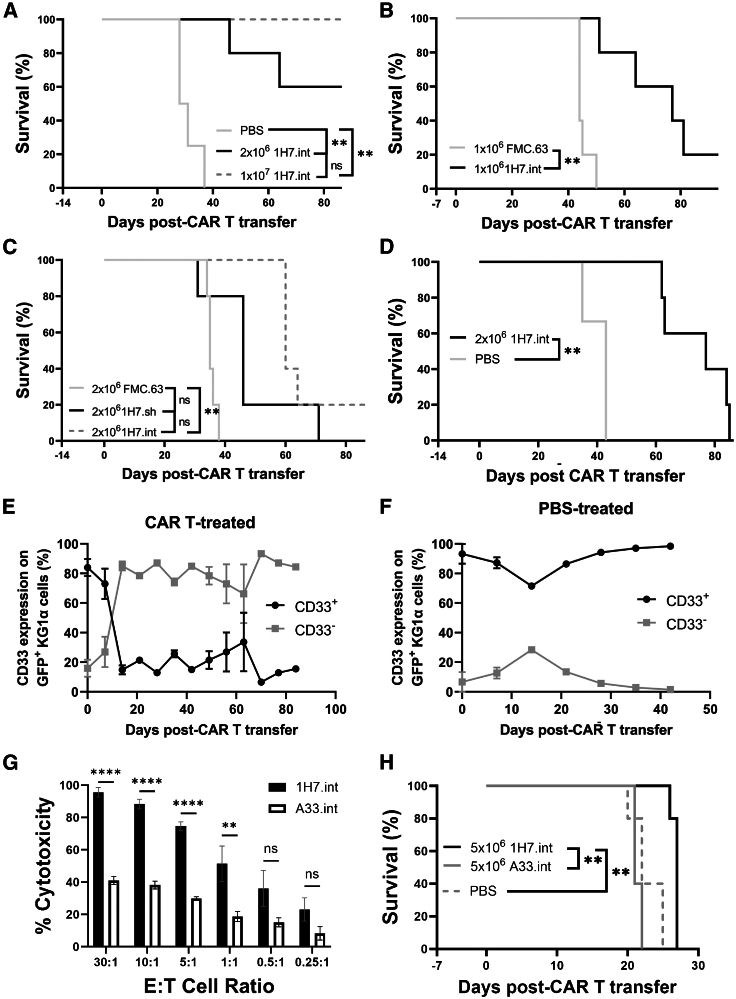
Figure 5.
In vivo activity of 1H7 CD33PAN CAR T cells
Immunodeficient NSG mice were injected with GFP-expressing HL-60 (A–C), KG-1a (D), or MOLM-14 (E) cells. (A) Survival of mice bearing HL-60 cells that received either 2 × 106 1H7.int, 1 × 107 1H7.int, or vehicle (PBS) control 2 weeks after transplantation of 2 × 106 HL-60 cells (n = 5 per HL-60 group, n = 4 in PBS group). (B) Survival of mice bearing HL-60 cells that received either 1 × 106 1H7.int or 1 × 106 FMC63 CAR T cells 1 week after receiving 1 × 106 HL-60 cells (n = 5 per group). (C) Survival of mice bearing HL-60 cells that received either 2 × 106 1H7.int, 2 × 106 1H7.sh, or 2 × 106 FMC63 CAR T cells 2 weeks after receiving 2 × 106 HL-60 cells (n = 5 per group). (D) Survival of mice bearing KG-1a cells having received either 2 × 106 CAR T cells or vehicle control 2 weeks following transfer of 2 × 106 KG-1a cells (n = 5 in KG-1a group, n = 3 in PBS group). (E) CD33 expression on GFP+ KG-1a AML cells in peripheral blood as measured by flow cytometry in mice that received 2 × 106 1H7 CAR T cells or (F) PBS control. (G) CD8+ CD33PAN (1H7.int) or CD33V-set (A33.int) CAR T cells were co-cultured with MOLM-14 cells at various E:T cell ratios as indicated and assessed for cytotoxicity by chromium-51 release 4 h later. Shown are mean ± SEM from technical triplicates. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns (not significant) by two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey correction. (H) Survival of NSG mice injected with 5 × 105 firefly luciferase-expressing MOLM-14 that then received CD33PAN (1H7.int) or CD33V-set (A33.int) 5 × 106 CAR T cells in a 1:1 ratio of CD4:CD8 T cells 1 week later by tail vein injection (n = 5 per group). Shown are mean ± SEM. ∗∗p < 0.01; ns (not significant) by log rank test.