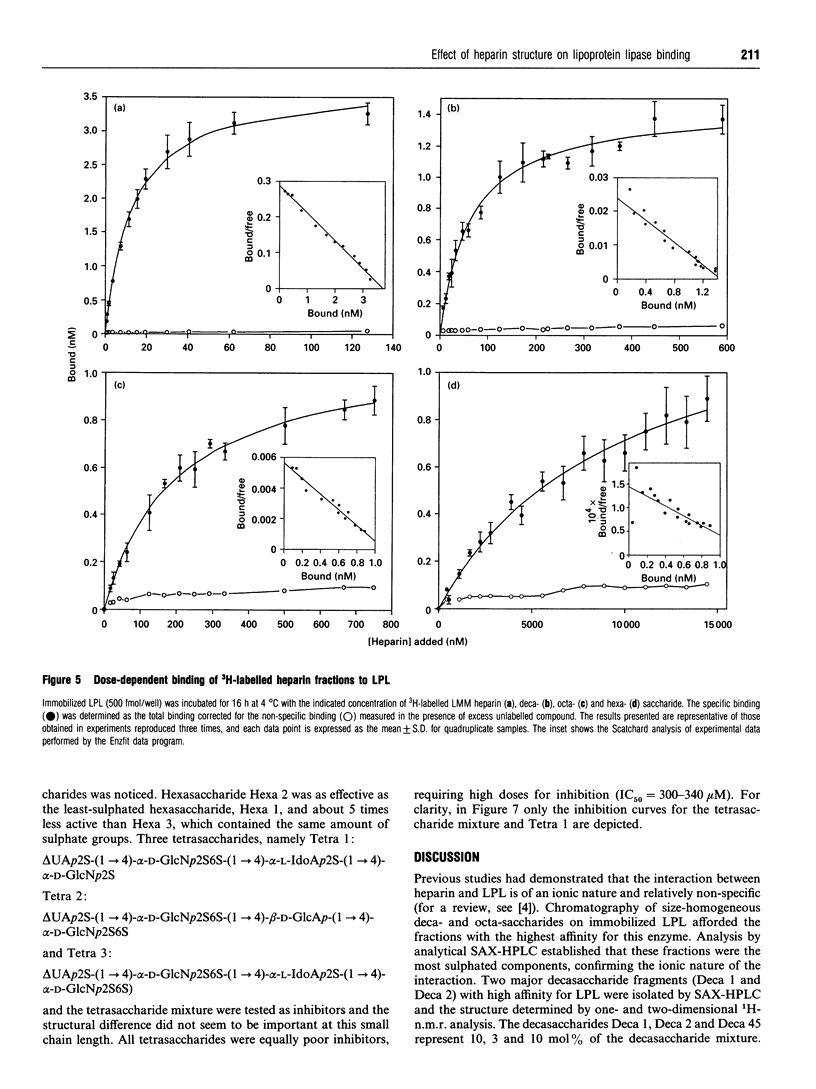
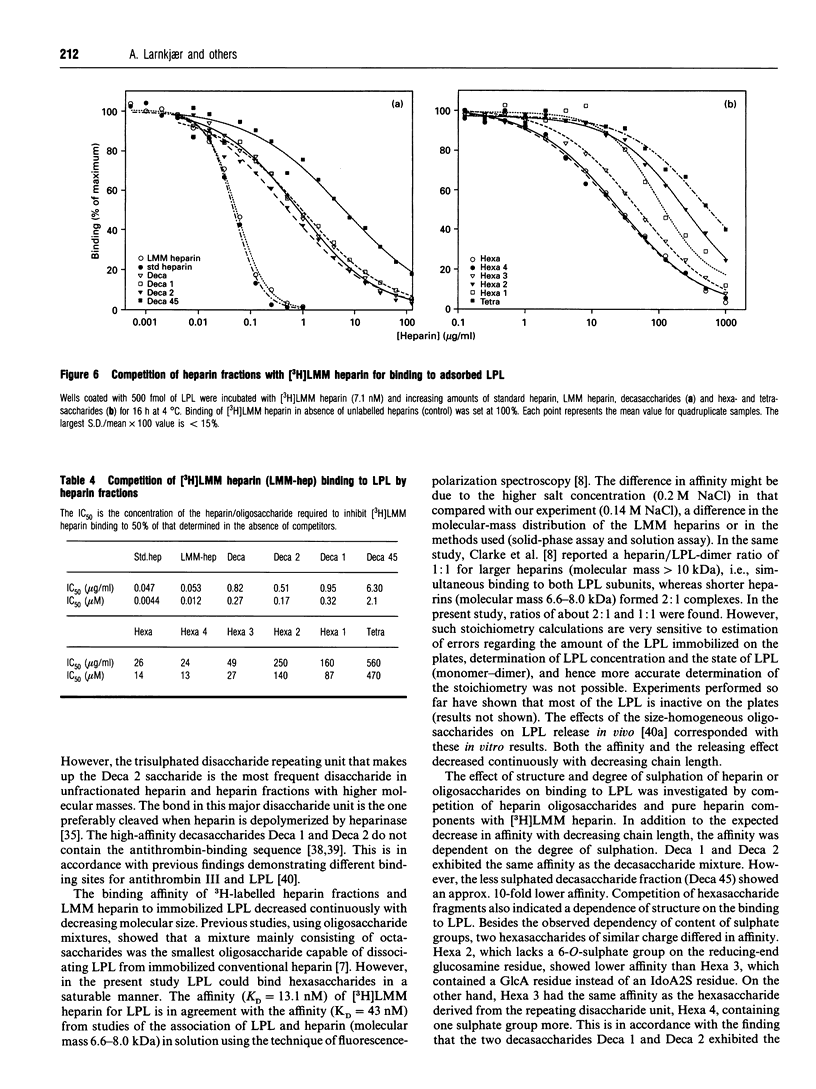
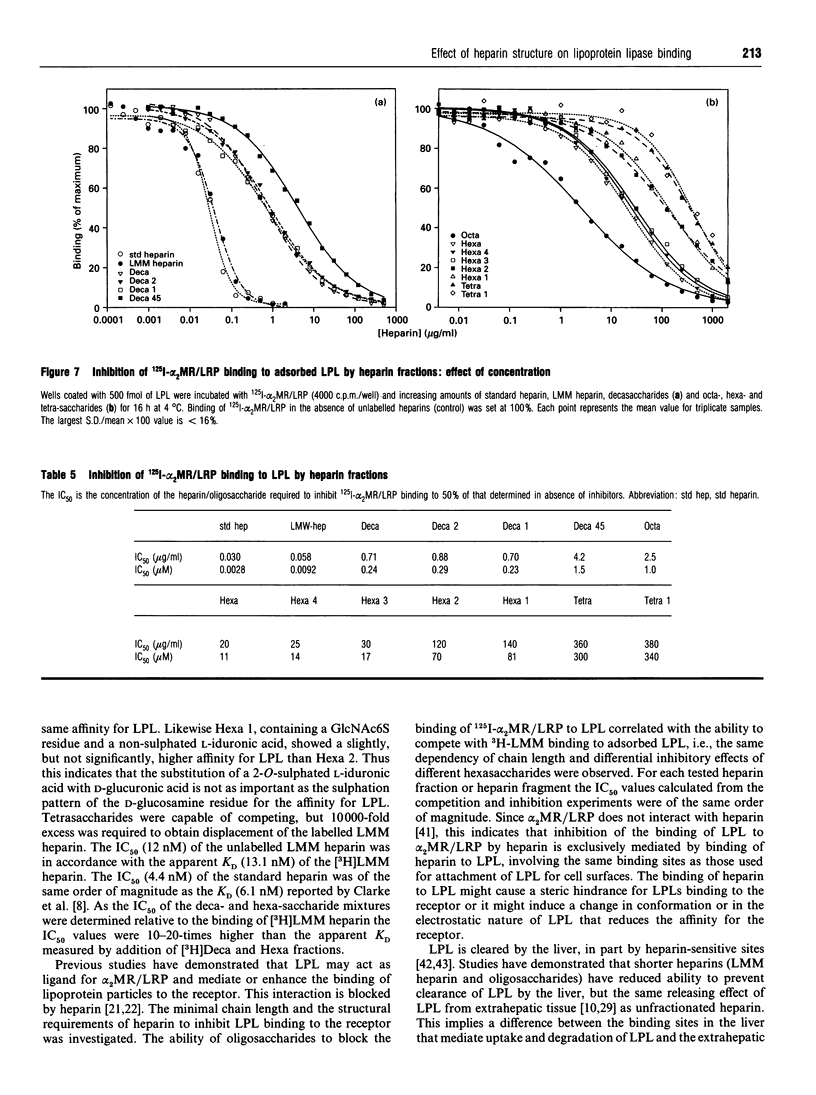
Abstract
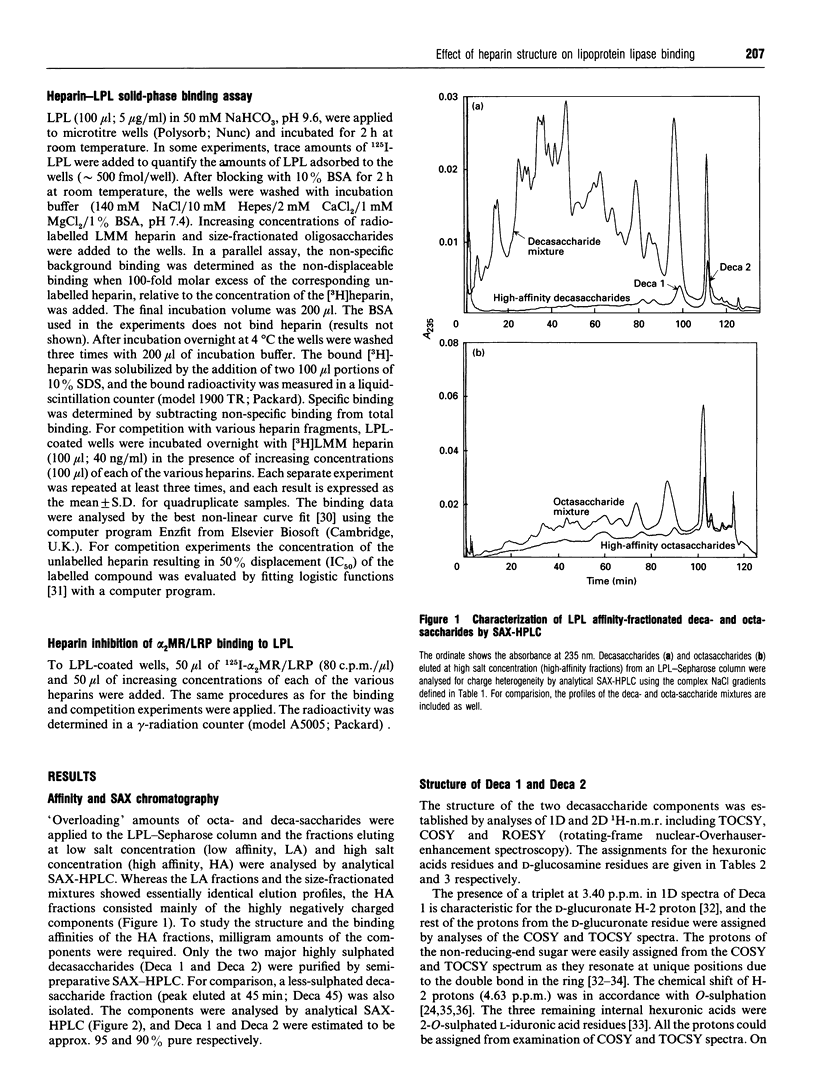
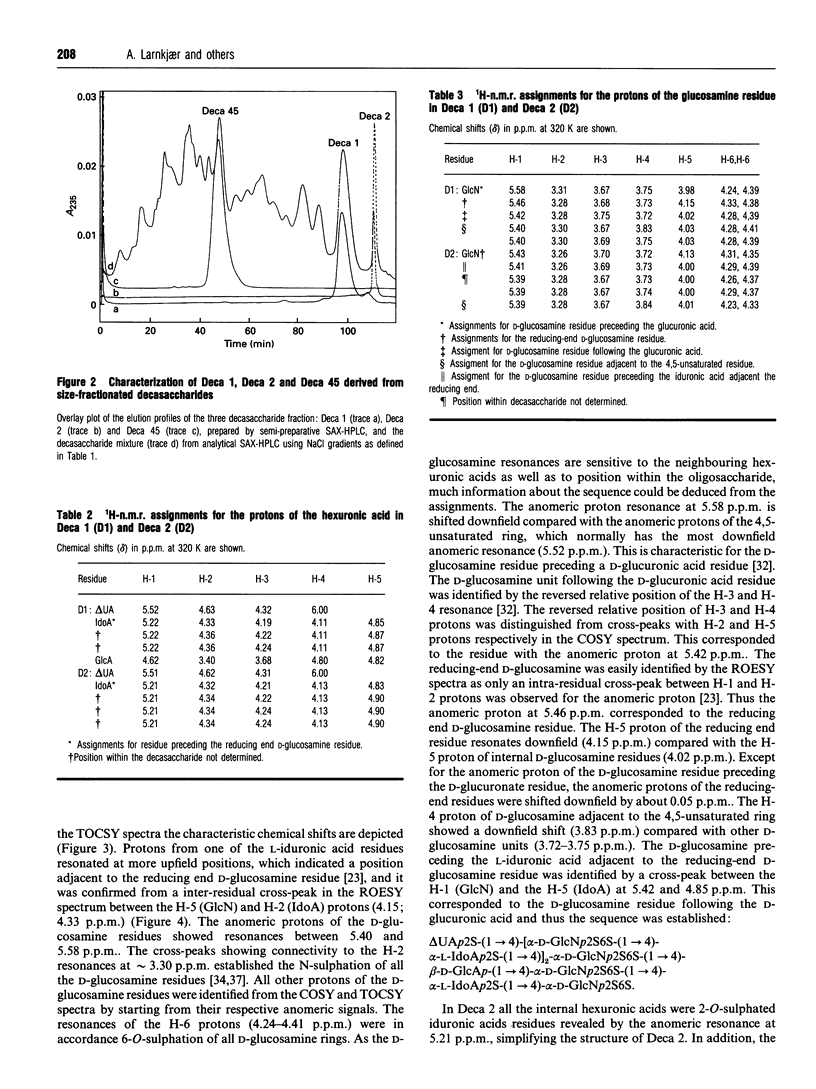
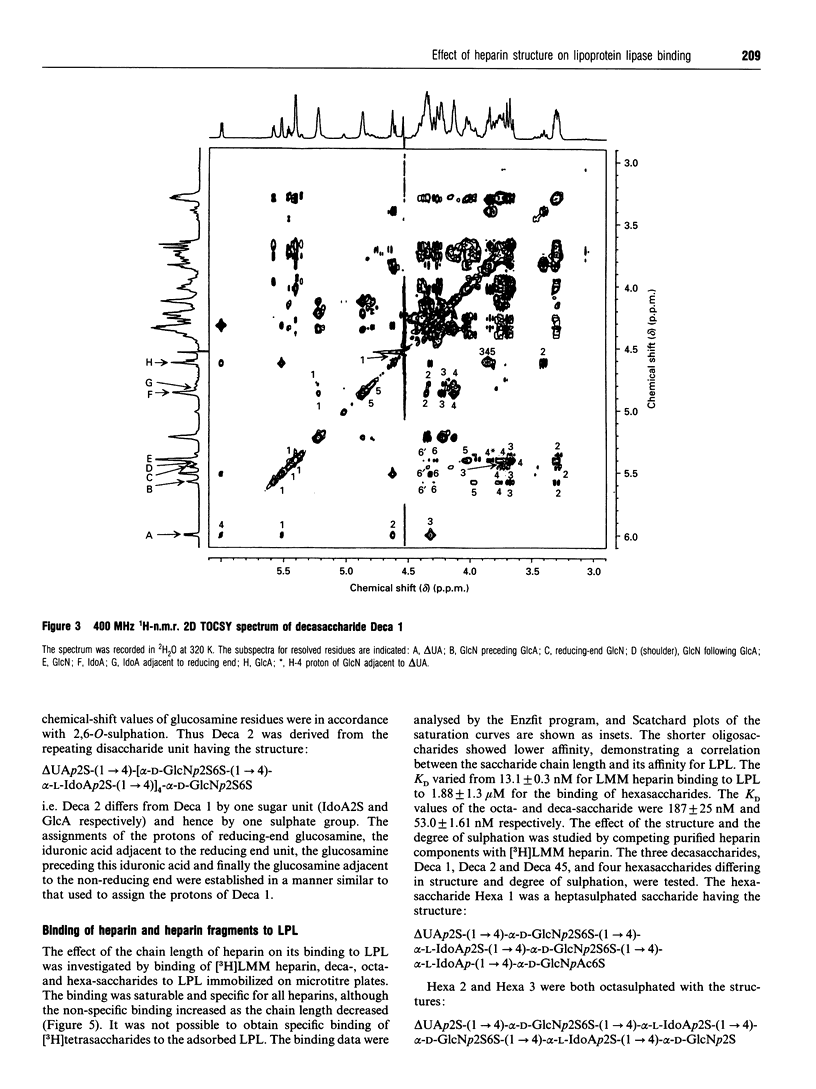
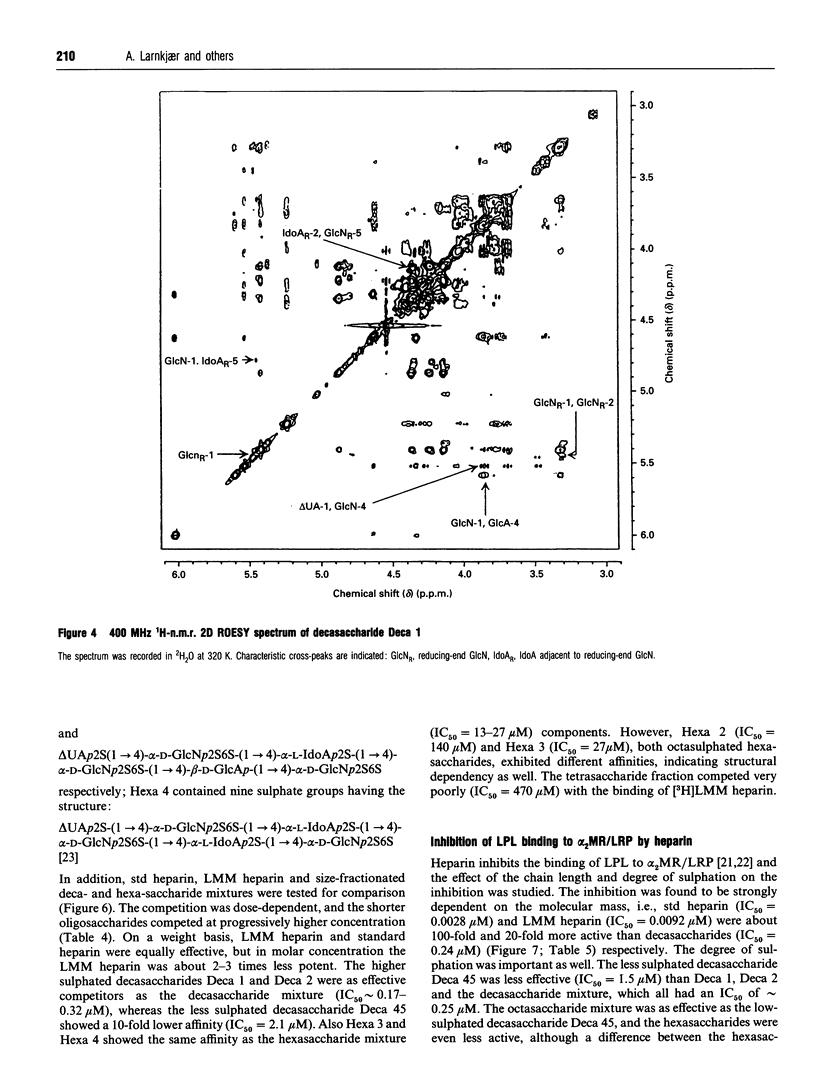
Heparin-derived deca- and octa-saccharides were subjected to affinity chromatography on lipoprotein lipase-Sepharose and the fractions eluted at high salt concentration were analysed by strong-anion-exchange chromatography. Two high-affinity decasaccharides were isolated and the structure determined by one- and two-dimensional 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy. The affinities of 3H-labelled low-molecular-mass heparin and size-fractionated deca-, octa-, and hexa-saccharides for lipoprotein lipase immobilized on microtitre plates were determined from saturation curves. From competition experiments the affinities of unlabelled heparins and pure deca- and hexa-saccharide fragments were determined. The binding was size- and charge-dependent, but structural dependency was also indicated. Thus substitution of a 2-O-sulphated L-iduronic acid with D-glucuronic acid was less important than the sulphation pattern of the D-glucosamine residue for affinity for lipoprotein lipase. Heparin inhibits binding of lipoprotein lipase to alpha 2-macroglobulin-receptor/low-density-lipoprotein receptor-related protein. The effects of size, charge and structure for this inhibition were studied. The ability of the heparin fragments to inhibit binding correlated with their affinity for lipoprotein lipase. This indicates that the inhibition of the binding of lipoprotein lipase to alpha 2-macroglobulin-receptor/low-density-lipoprotein receptor-related protein by heparin is exclusively mediated by binding of heparin to lipoprotein lipase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atha D. H., Stephens A. W., Rosenberg R. D. Evaluation of critical groups required for the binding of heparin to antithrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Lipoprotein lipase enhances the binding of chylomicrons to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8342–8346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Phospholipase activity of milk lipoprotein lipase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:345–356. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97160-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T., Hök M., Riesenfeld J., Lindahl U. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with native and modified heparin-like polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1890625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Interaction of heparin with proteins. Demonstration of different binding sites for antithrombin and lipoprotein lipase. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80350-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A. Lipoprotein lipase. Annu Rev Nutr. 1991;11:217–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.11.070191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J. E., Severson D. L. Release of lipoprotein lipase from cardiac myocytes by low-molecular weight heparin. Lipids. 1993 Jan;28(1):59–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02536362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Weintraub H. J. Molecular modeling of protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):21–32. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu B., Oreste P., Torri G., Zoppetti G., Choay J., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Sinäy P. The structure of heparin oligosaccharide fragments with high anti-(factor Xa) activity containing the minimal antithrombin III-binding sequence. Chemical and 13C nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):599–609. doi: 10.1042/bj1970599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Luscombe M., Holbrook J. J. The effect of the chain length of heparin on its interaction with lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 14;747(1-2):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H. Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1060–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata A., Ridinger D. N., Sutherland S., Emi M., Shuhua Z., Myers R. L., Ren K., Cheng T., Inoue I., Wilson D. E. Binding of lipoprotein lipase to heparin. Identification of five critical residues in two distinct segments of the amino-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8447–8457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne A., Gettins P. 1H-N.m.r. spectral assignments for two series of heparin-derived oligosaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1992 Feb 17;225(1):43–57. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(92)80038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuda S., Boyd H. C., Fligner C., Ross R., Gown A. M. Human atherosclerosis. III. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cell composition of lesions of young adults. Am J Pathol. 1992 Apr;140(4):907–914. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10771–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen H. I., Tromborg E. M., Nielsen J. R., Nielsen J. I., Johansen K. B., Ostergaard P. B. Development and validation of a size exclusion chromatography method for determination of molecular masses and molecular mass distribution in low molecular weight heparin. Thromb Res. 1991 Oct 15;64(2):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90113-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larnkjaer A., Hansen S. H., Ostergaard P. B. Isolation and characterization of hexasaccharides derived from heparin. Analysis by HPLC and elucidation of structure by 1H NMR. Carbohydr Res. 1995 Jan 3;266(1):37–52. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(94)00247-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larnkjaer A., Ostergaard P. B., Flodgaard H. J. Binding of low molecular weight heparin (Tinzaparin sodium) to bovine endothelial cells in vitro. Thromb Res. 1994 Jul 15;75(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt R. J., Wang H. M., Loganathan D., Bae J. H. Search for the heparin antithrombin III-binding site precursor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2380–2387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G. Q., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Ostergaard P., Olivecrona T. Low-Mr heparin is as potent as conventional heparin in releasing lipoprotein lipase, but is less effective in preventing hepatic clearance of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):747–752. doi: 10.1042/bj2730747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Hultin M., Ostergaard P., Olivecrona T. Interaction of size-fractionated heparins with lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in the rat. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 1;285(Pt 3):731–736. doi: 10.1042/bj2850731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loganathan D., Wang H. M., Mallis L. M., Linhardt R. J. Structural variation in the antithrombin III binding site region and its occurrence in heparin from different sources. Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4362–4368. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund H., Takahashi K., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Lipoprotein binding and endosomal itinerary of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9318–9322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant Z. M., Erbe E. E., Eddy W. P., Patel D., Linhardt R. J. Effect of very low molecular weight heparin-derived oligosaccharides on lipoprotein lipase release in rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Nov;62(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant Z. M., Kim Y. S., Rice K. G., Linhardt R. J. Structure of heparin-derived tetrasaccharides. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):369–377. doi: 10.1042/bj2290369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J. Analysis of ligand recognition by the purified alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor (low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein). Evidence that high affinity of alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complex is achieved by binding to adjacent receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14011–14017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Pallesen G. Distribution of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Sep;269(3):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00353892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Lookene A., Moestrup S. K., Petersen C. M., Weber W., Beisiegel U., Gliemann J. The alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein binds lipoprotein lipase and beta-migrating very low density lipoprotein associated with the lipase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15048–15055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Lee N. S., Olivecrona T. Studies on inactivation of lipoprotein lipase: role of the dimer to monomer dissociation. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5606–5611. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson E., Nordenström J., Nilsson-Ehle P., Hagenfeldt L. Lipolytic and anticoagulant activities of a low molecular weight fragment of heparin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;15(4):215–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1985.tb00171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitou M., Lormeau J. C., Perly B., Berthault P., Bossennec V., Sié P., Choay J. Is there a unique sequence in heparin for interaction with heparin cofactor II? Structural and biological studies of heparin-derived oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8685–8690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L. Alpha-macroglobulins: structure, shape, and mechanism of proteinase complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11539–11542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Llobera M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase uptake by the liver: localization, turnover, and metabolic role. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):G711–G722. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.5.G711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallinder L., Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Hepatic and extrahepatic uptake of intravenously injected lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 4;795(3):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallinder L., Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Hepatic and extrahepatic uptake of intravenously injected lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 4;795(3):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wion K. L., Kirchgessner T. G., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C., Lawn R. M. Human lipoprotein lipase complementary DNA sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1638–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.3823907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Yoshida K., Sugiura M., Sugahara K., Khoo K. H., Morris H. R., Dell A. Structural studies on the bacterial lyase-resistant tetrasaccharides derived from the antithrombin III-binding site of porcine intestinal heparin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4780–4787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Lipton B. A., Rosenfeld M. E., Goldberg I. J., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Macrophages and smooth muscle cells express lipoprotein lipase in human and rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10143–10147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


