Figure 4.
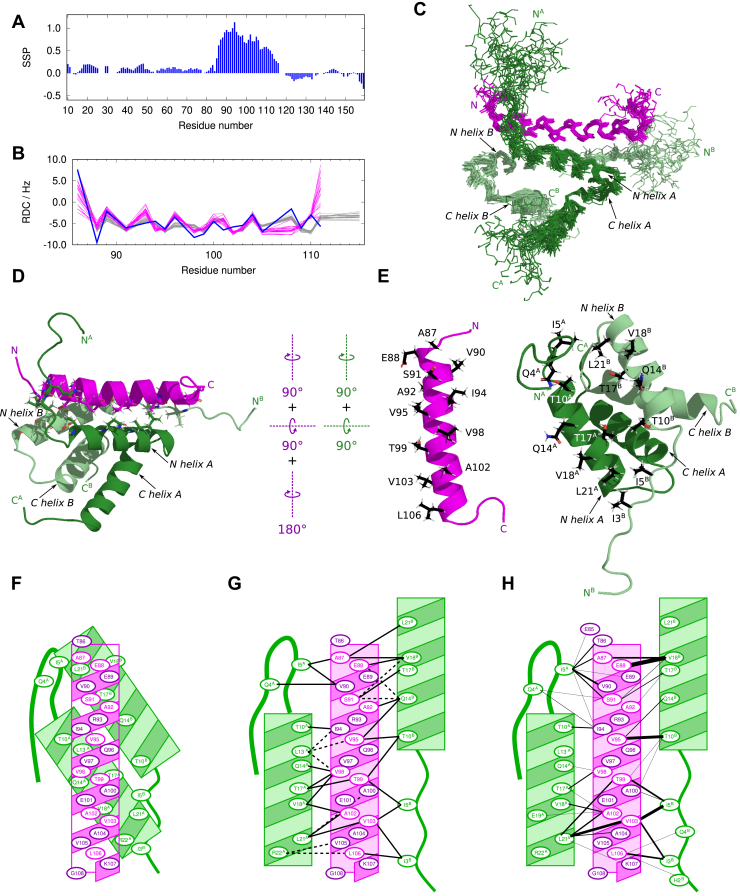
Solution structure of the N-MAP2c:RIIDD2complex.A, SSP of N-MAP2c residues in the complex. B, experimental (blue) 1H-15N RDC values of the helical part of N-MAP2c in the complex compared with values calculated from 20 refined structures (magenta) and from 25 structures predicted by AlphaFold multimer (gray). C, backbone traces of a set of 20 superimposed refined N-MAP2c:RIIDD2 structures. N-MAP2c, RIIDD2 protomers A and B are shown in magenta, pale green, and forest green, respectively. D, a representative refined structure of N-MAP2c:RIIDD2 colored as in panel C. Side chains of residues involved in the intermolecular contacts are depicted as sticks. E, the same structure as in panel D rotated by 90° about the vertical and horizontal axes and with the N-MAP2c helix further rotated by 180° to reveal the binding interface. Side chains of amino acids involved in the intermolecular contacts are depicted as sticks and labeled with single-letter codes. The N-terminal and C-terminal helices of RIIDD2 are labeled as N helix and C helix, respectively. F, schematic drawing of the orientation of the N-MAP2c (magenta) and RIIDD2 (green) helices. G, contacts between N-MAP2c and RIIDD2 helices. Solid and dashed black lines represent contacts observed in all 20 structures of the refined ensemble and only in some structures of the ensemble, respectively. H, intermolecular distance restraints derived from the measured NOE values shown as black lines. The width of the line is proportional to the number of restraints per an amino-acid pair (ranging from 1 to 20). Side chains oriented towards the interface are presented in magenta and forest green; side chains oriented away from the interface are shown in purple.