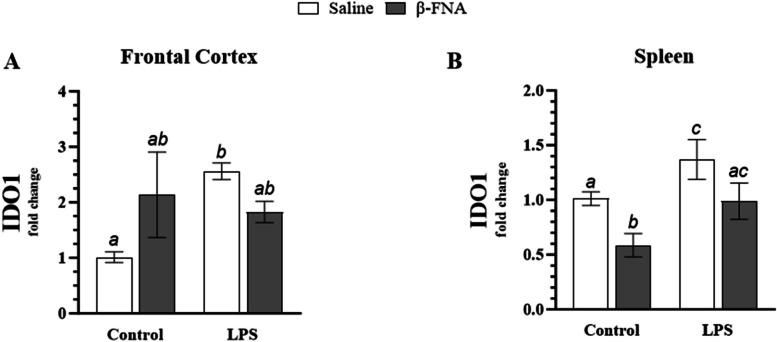
Fig. 10.
Chronic β-FNA effects on LPS-induced IDO1 expression in male C57BL/6J frontal cortex and spleen tissues. Micro-osmotic pumps containing saline or β-FNA (42 μg/d) were surgically implanted and dispensed at a flow rate of 0.5 μL/h for 7d. 6d post-surgery, mice (n = 7–8/group) were injected (i.p.) with either 25 μL saline control or LPS (0.83 mg/kg). Behavioral tests were administered 24 h later, and termination followed immediately after. RNA was extracted from (A) frontal cortex and (B) spleen tissues, and NLRP3 expression was measured via RT-qPCR. Statistical analysis was performed using the ∆CT-∆CT method and reported as fold change relative to the control group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. A Two-way ANOVA (n = 4–5/group) revealed a significant interaction of main effects (p < 0.05) and no significant main effect for LPS (p = 0.13) or β-FNA (p 0.62) on IDO1 expression in the frontal cortex. B Two-way ANOVA (n = 4–7/group) indicated a significant main effect for LPS (p < 0.01) and β-FNA (p < 0.005), but no significant interaction of main effects (p = 0.87) on IDO1 expression in the spleen. Pairwise comparisons were assessed using Fisher's LSD test; bars with letters in common indicate data are not significantly different (p > 0.05)