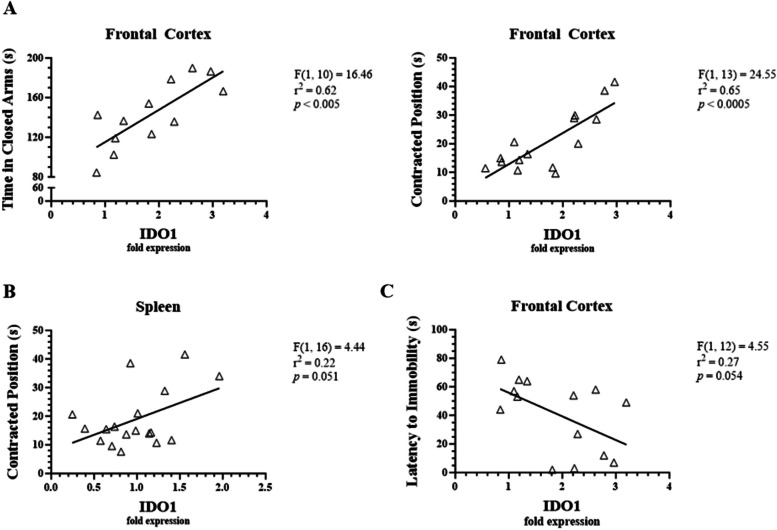
Fig. 12.
Correlations between LPS-induced IDO1 expression and behavioral measures in male C57BL/6J mice. Micro-osmotic pumps containing saline or β-FNA (42 μg/d) were surgically implanted and dispensed at a flow rate of 0.5 μL/h for 7d. 6d post-surgery, mice (n = 7–8/group) were injected (i.p.) with either 25 μL saline control or LPS (0.83 mg/kg). Behavioral tests were administered 24 h later, and termination followed immediately after. IDO1 was measured via RT-qPCR using frontal cortex and spleen RNA extracts. Linear regression analysis was used to assess frontal cortex and spleen NLRP3 expression with various anxiety-, sickness-, and depressive-like behavioral endpoints. A IDO1 in the frontal cortex correlated with anxiety- and sickness-like behavior. B IDO1 in the spleen trended with sickness-like behavior but fell short of significance. C IDO1 in the frontal cortex trended with depressive-like behavior but fell short of significance. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Linear regression statistics and symbols are provided in figure