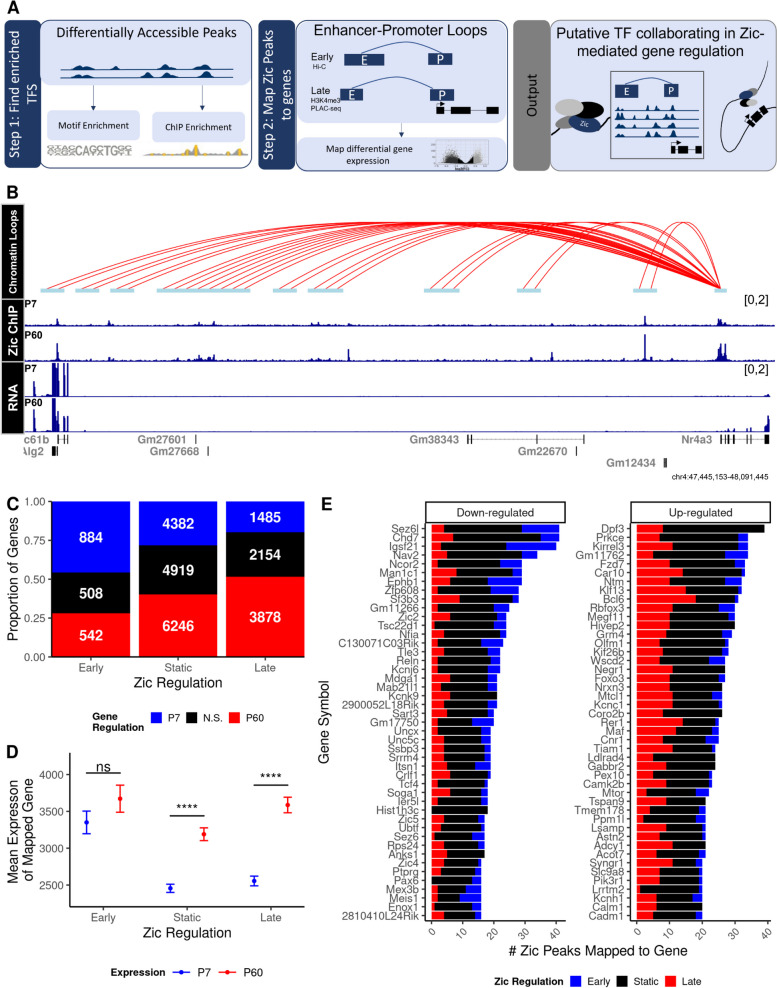
Fig. 3.
Zic binding sites can be mapped to genes through chromatin looping. Zic ChIP peaks were overlapped with anchors derived from cerebellar Hi-C [56] and H3K4me3 PLAC-seq [54] data. A Schematic of peak mapping workflow using chromatin looping data. B Example tracks of H3K4me3 loops interacting with the Nr4a3 gene 100 MB upstream, Zic ChIP-seq at P7 and P60, and RNA-seq at P7 and P60. C Overall number of genes mapped to early, static, and late Zic ChIP-seq peaks. D Expression of genes at P7 and P60 mapped to early, static, and late Zic ChIP-seq peaks. Graph shows mean and standard deviation of gene expression, *** denotes a significant difference in the mean expression between P7 and P60 with a Bonferroni adjusted p < 2.2e − 6 using a pairwise t-test. E Top 50 downregulated (FDR < 0.0f, LFC < 0) and upregulated (FDR < 0.05, LFC > 0) genes by the number of mapped Zic ChIP-seq peaks that are dynamic between P7 and P60. Red indicates ChIP-seq peaks enriched at P60 (late), blue indicates enriched at P7 (early), and black indicates static peaks