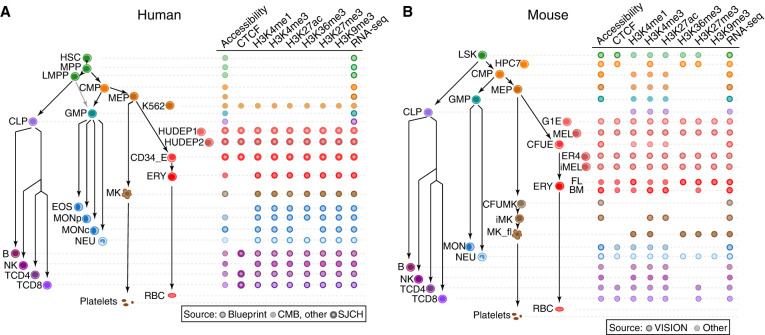
Figure 1.
Cell types and data sets used for systematic integration of epigenetic features of blood cells. (A) The tree on the left shows the populations of stem, progenitor, and mature blood cells and cell lines in human. The diagram on the right indicates the epigenetic features and transcriptomes for which genome-wide data sets were generated or collected, with distinctive icons for the major sources of data, specifically the Blueprint project (Martens and Stunnenberg 2013; Stunnenberg et al. 2016), Corces et al. (2016) (CMB), and St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (SJCRH) (Cheng et al. 2021; Qi et al. 2021). (B) Cell types and epigenetic data sets in mouse, diagrammed as for panel A. Sources were described by Xiang et al. (2020) (Supplemental Table S1). Abbreviations for blood cells and lines are as follows: (HSC) hematopoietic stem cell, (MPP) multipotent progenitor cell, (LMPP) lymphoid–myeloid primed progenitor cell, (CMP) common myeloid progenitor cell, (MEP) megakaryocyte–erythrocyte progenitor cell, (K562) a human cancer cell line with some features of early megakaryocytic and erythroid cells, (HUDEP) immortalized human umbilical cord blood–derived erythroid progenitor cell lines expressing fetal globin genes (HUDEP1) or adult globin genes (HUDEP2), (CD34_E) human erythroid cells generated by differentiation from CD34+ blood cells, (ERY) erythroblast, (RBC) mature red blood cell, (MK) megakaryocyte, (GMP) granulocyte monocyte progenitor cell, (EOS) eosinophil, (MON) monocyte, (MONp) primary monocyte, (MONc) classical monocyte, (NEU) neutrophil, (CLP) common lymphoid progenitor cell, (B) B cell, (NK) natural killer cell, (TCD4) CD4+ T cell, (TCD8) CD8+ T cell, (LSK) Lin−Sca1+Kit+ cells from mouse bone marrow containing hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, (HPC7) immortalized mouse cell line capable of differentiation in vitro into more mature myeloid cells, (G1E) immortalized mouse cell line blocked in erythroid maturation by a knockout of the Gata1 gene and its subline ER4 that will further differentiate after restoration of Gata1 function in an estrogen-inducible manner (Weiss et al. 1997), (MEL) murine erythroleukemia cell line that can undergo further maturation upon induction (designated iMEL), (CFUE) colony forming unit erythroid, (FL) designates ERY derived from fetal liver, (BM) designates ERY derived from adult bone marrow, (CFUMK) colony forming unit megakaryocyte, (iMK) immature megakaryocyte, and (MK_fl) megakaryocyte derived from fetal liver.