Figure 4.
PMA treatment unlocks engraftment potential in 12 HPT-HBCs
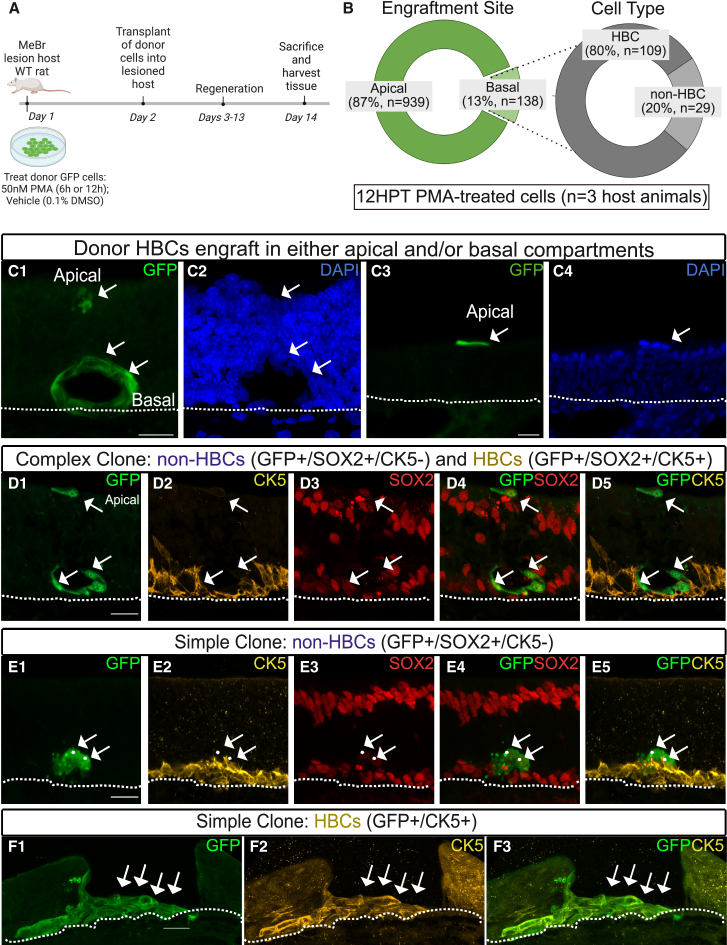
(A) Schematic illustration of transplantation assay.
(B) Quantification of 12 HPT PMA-treated GFP+ HBCs (n = 1077) based on engraftment location: apical (n = 939 total cells) or basal (n = 138 total cells). n = 3 host rats. Quantification of 12H PMA-treated basal cells (n = 138) based on progeny outcome (HBC or non-HBC).
(C1–C4) Representative clones highlighting GFP engraftment sites (apical and/or basal). Scale bars: 20 μm.
(D1–D5) Representative complex clone comprising HBCs (GFP+/SOX2+/CK5+) and GBCs (GFP+, SOX2+, CK5-). Note representative unengrafted HBC atop the apical cell layer. Scale bar: 20 μm.
(E1–E5) Representative simple clone comprising non-HBCs (GFP+, SOX2+, CK5-). Scale bar: 20 μm.
(F1–F3) Representative oversized simple clone highlighting a swathe of engrafted HBCs. Note missing apical structures. Scale bar: 20 μm.