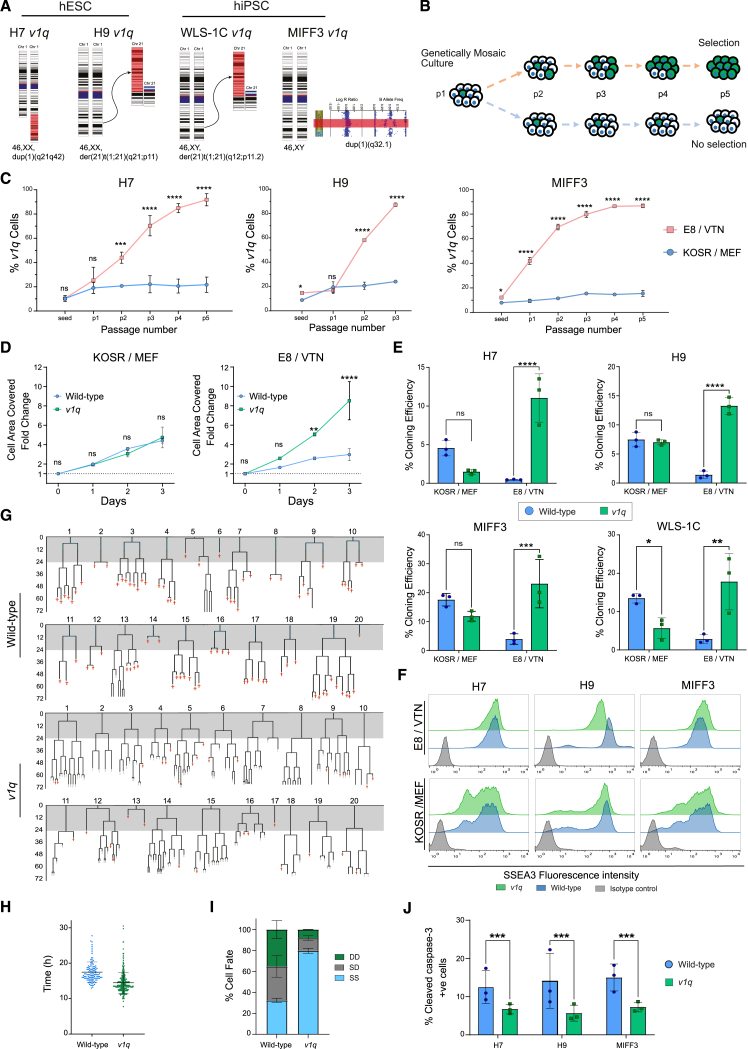
Figure 4.
v1q have selective advantage in KOSR-free but not KOSR-based conditions
(A) A panel of wild-type and v1q sublines across four genetic backgrounds (H7, H9, MIFF3, and WLS-1C) used in this study.
(B) Selective advantage was tested by mixing ∼10% v1q with their wild-type counterparts, with either of the lines being fluorescently labeled. Mixed cells were plated into either KOSR/MEF or E8/VTN, and the ratio of variants was monitored over subsequent passages.
(C) v1q overtake wild-type cells rapidly in E8/VTN but not in KOSR/MEF. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ns, non-significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA.
(D) v1q have a significantly higher growth rate than wild-type cells in E8/VTN but not KOSR/MEF. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ns, non-significant; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA.
(E) v1q have a significantly higher cloning efficiency than wild-type cells in E8/VTN but not KOSR/MEF. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ns, non-significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. two-way ANOVA, Fisher’s least significant difference.
(F) Wild-type and v1q hPSCs display similar levels of expression of a marker of undifferentiated state, SSEA3, in E8/VTN and in KOSR/MEF conditions.
(G) Lineage trees tracked from time-lapse images of wild-type cells (upper two panels) and v1q (lower two panels). Red crosses indicate cell death. Gray-shaded area indicates the first 24 h post-plating when the cells were grown in the presence of Y-27632, required for single-cell passaging.
(H) v1q show a trend toward a faster cell-cycle time compared to wild-type counterparts. Data points indicate 114 and 286 divisions for wild-type and v1q cells, respectively, from two independent experiments.
(I) Percentage of cell fate outcomes of daughter cells following cell division, with SS denoting survival of both daughter cells, SD survival of one and death of the other daughter cell, and DD death of both daughter cells.
(J) v1q have decreased levels of cleaved caspase-3 marker of apoptosis. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test. See also Video S1 and Figure S6.