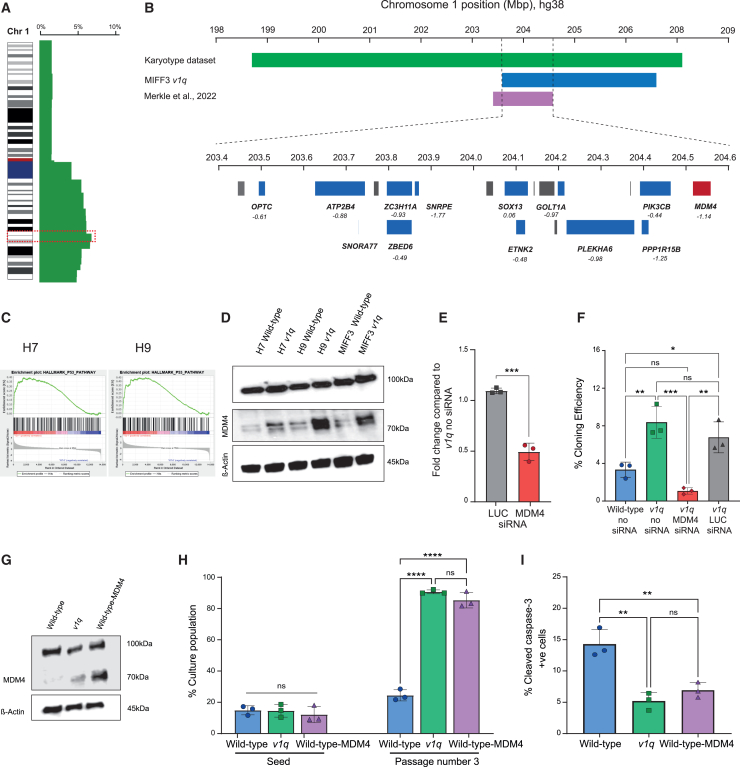
Figure 5.
MDM4 overexpression provides selective advantage to v1q
(A) The minimal region on chromosome 1q32.1 identified from the karyotyping datasets in this study.
(B) The minimal region on chromosome 1q32.1 identified from overlaying the karyotyping datasets in this study, SNP array data from MIFF3 v1q used in this study, and data published by (Merkle et al., 2022). The minimal amplicon contains 13 genes expressed in hPSCs (blue boxes), which were compared based on their essentiality scores (indicated in italics underneath the genes; for comparison, an essentiality score for POU5F1 is −1.85). MDM4 (red) is a candidate of interest, based on its known role in p53 signaling and cancer.
(C) RNA-seq analysis of H7 and H9 v1q versus wild-type sublines revealed differential expression of the p53 pathway.
(D) MDM4 expression is increased in v1q. Western blot analysis of H7, H9, and MIFF3 wild-type and v1q cells. β-actin was used as a loading control.
(E) Knockdown of MDM4 with small interfering RNA (siRNA) in v1q was confirmed by quantitative PCR. siRNA for Renilla Luciferase (siRNA LUC) was used as a negative control. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; Student’s t test.
(F) MDM4 knockdown suppresses cloning efficiency of v1q. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ns, non-significant, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; One-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test.
(G) Overexpression of MDM4 in wild-type hPSCs. Western blot analysis of MIFF3, MIFF3 v1q, and MIFF3 wild-type cells overexpressing MDM4 (wild-type-MDM4). β-actin was used as a loading control.
(H) MDM4 overexpression provides selective advantage to wild-type hPSCs. Mixed cultures were analyzed at seeding and after three passages. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ns, non-significant, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001; One-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test.
(I) MDM4 overexpressing and v1q cells have lower percentage of cleaved caspase-3 marker of apoptosis compared to wild-type counterparts. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ns, non-significant, ∗∗p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test.