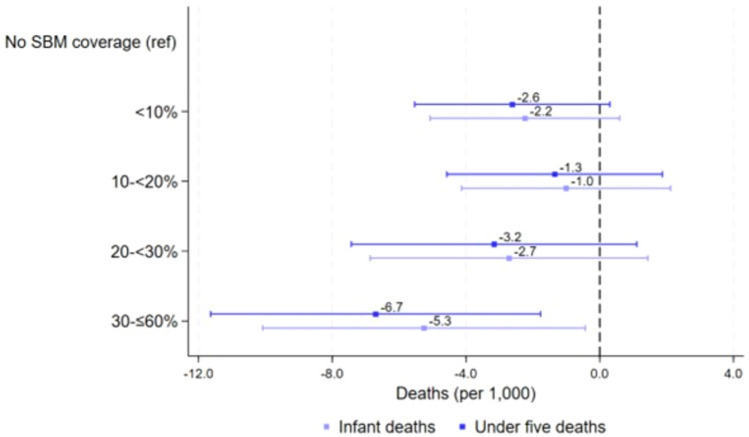
Fig. 5.
Panel data analysis examining the relationship between intensity of exposure to SBM and infant and child mortality. Note: A categorical variable was created using mean SBM coverage among households at the district-level with the following categories: 0%, > 0 and < 10%, 10 to < 20%, 20 to < 30%, and ≤ 60% coverage between 2015 and 2020. The reference group was districts with no toilets constructed under SBM in a particular year between 2015 and 2020. The model includes district-level controls for child birth order, maternal education, religion, caste, access to health services and insurance, and household wealth, cooking fuel, and piped water access. The model includes district-level fixed effects and standard errors are clustered at the district-level.