Table 1.
Epistatic score predictions for 80 previously classified CACNA1D variants based on model 3.
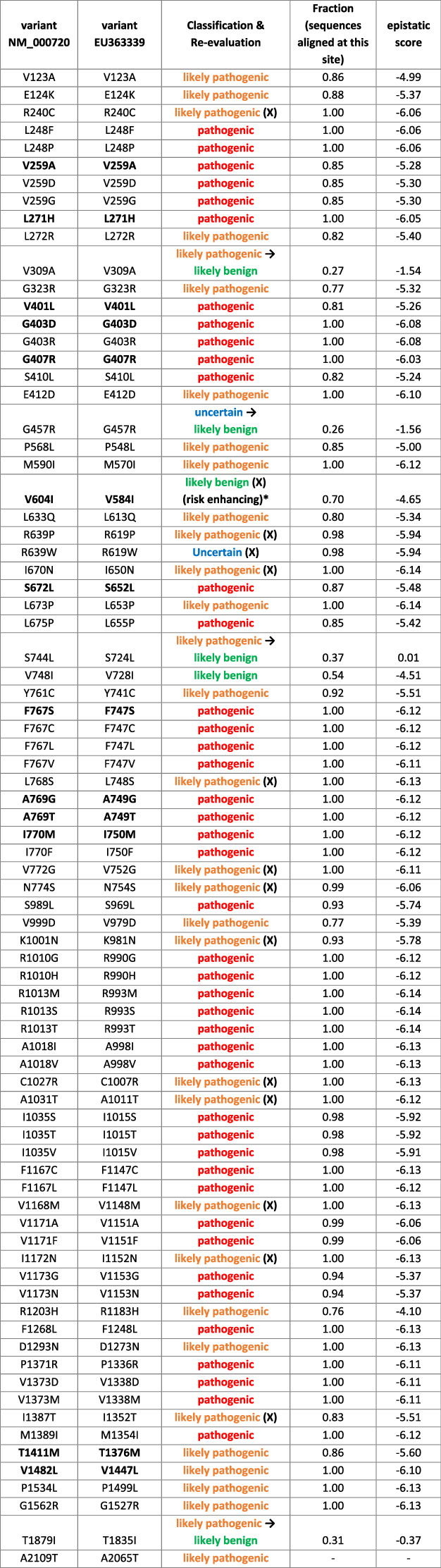
The table of variants collected by us previously [2, 3] shows the original pathogenicity annotation as well as statistical details on model predictions. Re-evaluation, i.e., re-classification and re-examination (SI Table 1) are marked with → and (X). Reassessment of the literature based on additional criteria triggered by the epistatic score revealed further evidence supporting or not supporting either pathogenicity or non-pathogenicity for some variants as outlined in detail in SI Table 3. De novo CACNA1D variants were either found somatically in adrenal lesions (APAs/APCCs) or in the germline of individuals with a neurodevelopmental disorder (indicated in bold). Residue numbers are given for the genome reference sequence used in the gnomAD database (NM_000720) or in our previous publications (EU363339), which differ due to the incorporation of different exons. The fraction of sequences aligned at the corresponding position scores the certainty of the prediction.
*V584I shows typical pathogenic gating changes (activation at more negative voltages; Fig. 3), however, to a minor extent compared to clearly pathogenic variants, suggesting it to be a risk enhancer rather than a pathogenic variant.
