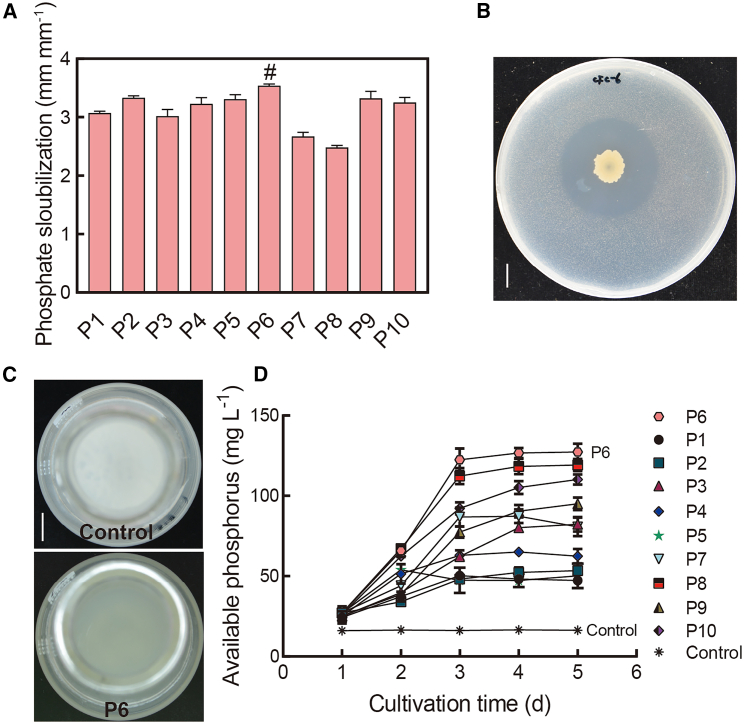
Figure 3.
Pseudomonas sp. (P6), isolated from the roots of OsPHR2 OE rice, shows high phosphate solubilization ability.
(A) Phosphate solubilization ability of 10 bacterial strains isolated from OsPHR2 OE roots and grown on Pikovskaya’s agar medium. Phosphate solubilization efficiency was calculated as solubilization zone (mm)/colony diameter (mm). The hash symbol (#) highlights the highest phosphate solubilization efficiency among the 10 isolates. Data are means ± SD (n = 3).
(B) Image of phosphate solubilization by P6. Bar: 1 cm.
(C and D) Available phosphorus concentrations in NBRIP liquid medium. The white sediment visible in the control treatment is Ca3(PO4)2, and the gray sediment in the P6-inoculation treatment indicates that some Ca3(PO4)2 has been solubilized by P6. Data are means ± SD (n = 3). Bar: 1 cm.