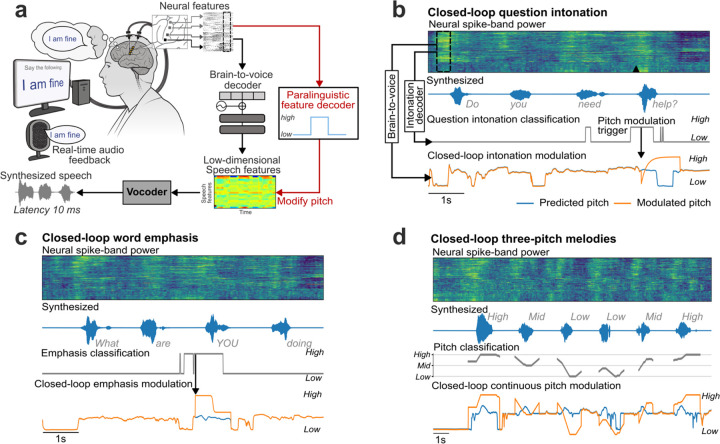
Extended Data Fig. 8: Closed-loop paralinguistic features modulation.
a. An overview of the paralinguistic feature decoder and pitch modulation pipeline. An independent paralinguistic feature decoder ran in parallel to the regular brain-to-voice decoder. Its output causally modulated the pitch feature predicted by brain-to-voice, resulting in a pitch-modulated voice. b. An example trial of closed-loop intonation modulation for speaking a sentence as a question. A separate binary decoder identified the change in intonation and sent a trigger (downward arrow) to modulate the pitch feature output of the regular brain-to-voice decoder according to a predefined pitch profile for asking a question (low pitch to high pitch). Neural activity of an example trial with its synthesized voice output is shown along with the intonation decoder output, time of modulation trigger (downward arrow), originally predicted pitch feature and the modulated pitch feature used for voice synthesis. c. An example trial of closed-loop word emphasis where the word “YOU” from “What are YOU doing” was emphasized. To emphasize a word, we applied a predefined pitch profile (high pitch to low pitch) along with a 20% increase in the loudness of the predicted speech samples. d. An example trial of closed-loop pitch modulation for singing a melody with three pitch levels. The three-pitch classifier output was used to continuously modulate the predicted pitch feature output from the brain-to-voice decoder.