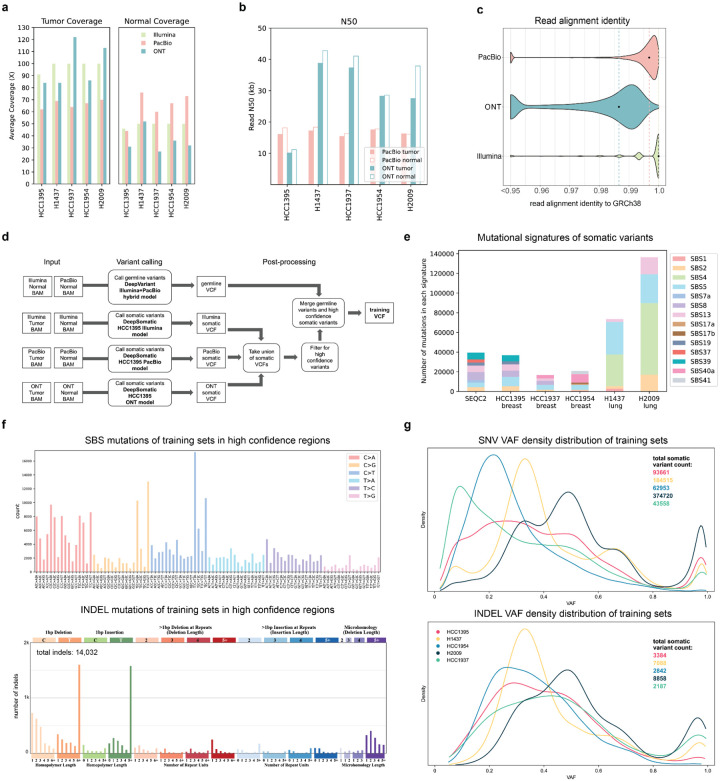
Figure 2: Training sets generated to train DeepSomatic.
(a) Average sequencing fold coverage per sample. (b) Read N50 for long-read samples. (c) Read alignment identity to GRCh38 reference. Points mark the median for each sequencing technology. (d) Steps to derive training sets using DeepSomatic HCC1395 models. (e) Mutational signature analysis of the SEQC2 benchmark and somatic variants in training sets in high confidence regions derived as described in (d). (f) In high confidence regions aggregated across all five cell lines, (top) numbers of single base somatic substitutions stratified by context (SBS-96), and (below) types of indel mutations. Plots were generated using SigProfileMatrixGenerator (Bergstrom et al. 2019) (g) Variant allele frequency (VAF) distribution of somatic variants in training sets in high confidence regions represented as a Kernel Density Estimate (KDE) plot.