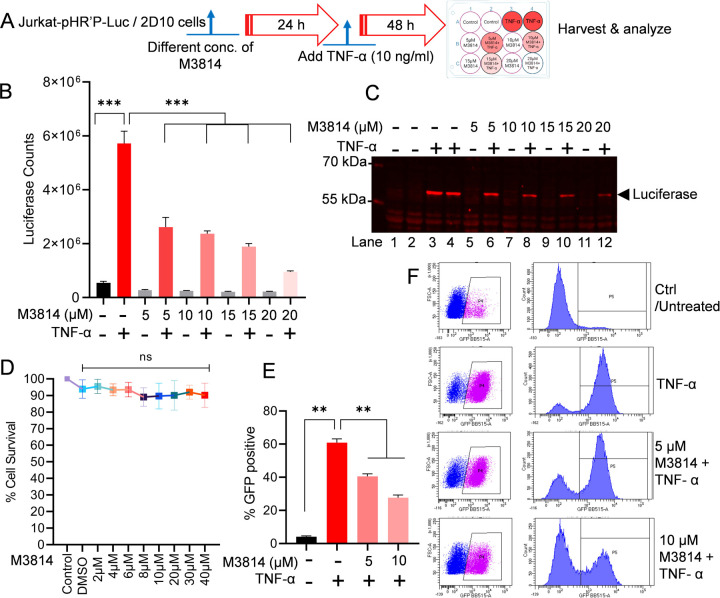
Figure 3: Partial DNA-PK inhibition severely impairs HIV transcription and latency reactivation.
Schematic representation of protocol for M3814 inhibitor and TNF-α treatment in the luciferase reporter assay (A). Jurkat-pHR’-P-Luc cells were treated with 5, 10, 15, and 20 µM of M3814 for 24 h, followed by activation with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for another 48 h. Cells were lysed, and the level of reporter protein expression was determined by a luciferase assay (B). The same lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using specific antibodies against the luciferase protein (sc-74548) (C). Jurkat-pHR’-P-Luc cells were cultured with different concentrations (2 μM to 40 μM) of M3814 for 48–72 h, and cell cytotoxicity was determined via MTS-PMS cell proliferation assay (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) (D). Latently HIV-infected 2D10 cells, which express the reporter short-lived green fluorescent protein (d2EGFP) from the HIV LTR promoter, were treated with 5 µM or 10 µM of M3814 for 24 h and then stimulated with TNF-α for another 48 h. Cells were subjected to GFP expression analysis via flow cytometry (E & F). Immunoblots are representative of at least three independent experiments The results are expressed as mean ± SD and analyzed by one- or two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Asterisks over the bars indicate significant differences: **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for the comparison of inactive vs. activated cells (TNF-α) and activated cells (TNF-α) vs. activated cells (TNF-α) in the presence of the DNA-PK inhibitor, M3814.