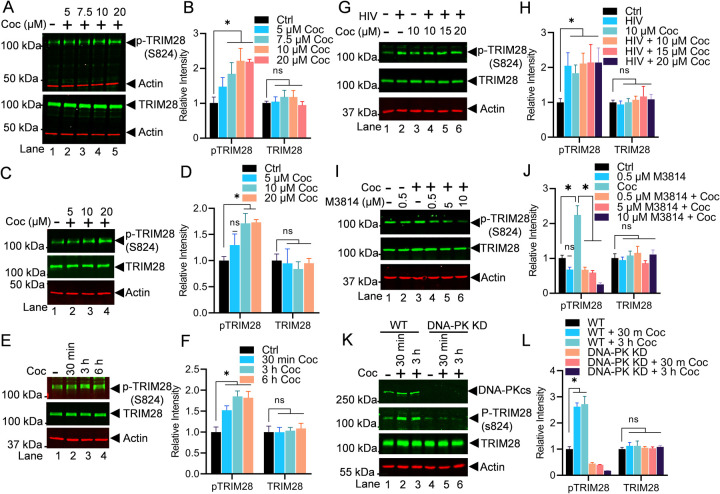
Figure 8: Cocaine-induced DNA-PK relieves RNAP II pausing by phosphorylating TRIM28 at S824.
THP-1 (A & B) and Jurkat cells (C & D) were treated with increasing doses of cocaine, and the nuclear lysates were analyzed via immunoblotting using specific antibodies against pTRIM28 (S824) and total TRIM28. Densitometric analysis confirmed a significant increase in pTRIM28 (S824) levels compared to untreated cells (Ctrl) (A, B, C & D). Jurkat-pHR’P-Luc cells were treated with cocaine (10 µM) for varying durations (30 min, 3 h, and 6 h), and the nuclear lysates were analyzed via immunoblotting using specific antibodies against pTRIM28 (S824) and total TRIM28. Densitometric analysis of protein bands (normalized to actin) confirmed a significant increase in pTRIM28 (S824) levels compared to untreated cells (Ctrl) (E & F). THP-1 cells were treated as follows: untreated and uninfected (Lane 1), infected with HIV (93/TH/051) without cocaine (Lane 2), treated with cocaine without HIV infection (Lane 3), or pre-treated with different concentrations of cocaine before HIV infection (Lanes 4 to 6). Nuclear lysates were analyzed via immunoblotting using specific antibodies against pTRIM28 (S824) and total TRIM28 (G). Densitometric analysis of protein bands (normalized to actin) confirmed a significant increase in pTRIM28 (S824) levels compared to untreated cells (Ctrl) (H). THP-1 cells were treated with different concentrations of M3814 in the presence and absence of cocaine (10 µM), and the nuclear lysates were analyzed via immunoblotting using specific antibodies against pTRIM28 (S824) and total TRIM28 (I). Densitometric analysis of protein bands (normalized to actin) confirmed a significant increase in pTRIM28 (S824) levels compared to untreated cells (Ctrl). However, the presence of the inhibitor (M3814) severely impaired pTRIM28 (S824) compared to the cocaine-treated sample (J). WT and DNA-PK KD cells were treated with cocaine for 30 min and 3 h, and nuclear lysates were subjected to immunoblotting (K). Densitometric analysis of protein bands (normalized to actin) confirmed enhanced phosphorylation of p-TRIM28 in WT cells upon cocaine exposure. However, in DNA-PK KD cells, phosphorylated TRIM28 levels remained reduced upon cocaine exposure, confirming that cocaine-induced TRIM28 phosphorylation is DNA-PK specific (L). Immunoblots are representative of at least three independent experiments. The results are expressed as mean ± SD for three independent experiments, analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Asterisks over the bars indicate significant differences. ∗p < 0.05 is for the comparison of cocaine-treated samples against untreated (Ctrl) and the comparison of cocaine plus inhibitors treated against cocaine alone-treated samples