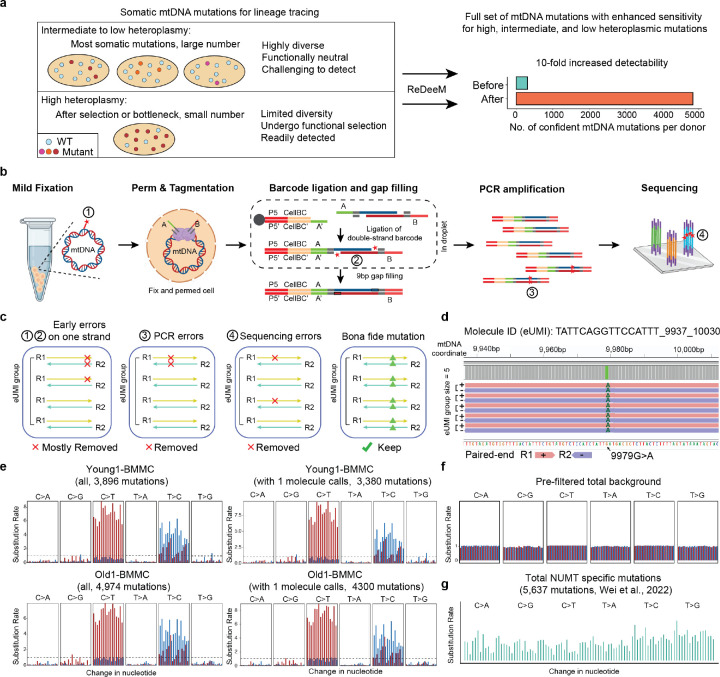
Fig. 1. Enhanced sensitivity of ReDeeM through rigorous single-molecule consensus.
(a) Challenge and motivation of enhancing mtDNA mutation detection. A large majority of somatic mtDNA mutations show intermediate to low heteroplasmy as many are associated with sub-clonal events. The advantages and limitations of different heteroplasmic mutations are discussed. ReDeeM allows detection of a fuller set of mtDNA mutations including high, intermediate, and low heteroplasmic mutations for fine-scale and unbiased lineage tracing. (b) Workflow of the ReDeeM experiment and the potential sources of artifacts within each experimental stage, represented as red stars. See more detailed discussion in Supplementary Notes. (c) Single-molecule consensus error correction strategy that accounts for previously described artifacts. See more detailed discussion in Supplementary Notes. (d) One real data example of the grouped eUMI sequencing read family. The eUMI group size is 5, each is completely overlapping sequenced by both R1 and R2. (e-g) Mutational signatures (frequency unweighted) for all ReDeeM identified confident mtDNA mutations or the collection for 1+-molecule mutations in Young1-BMMC and Old1-BMMC (also see Extended Data Fig. 1b). (e) In comparison, the mutational signatures for prefiltered mutations, and NUMT mutations are also shown (f-g)