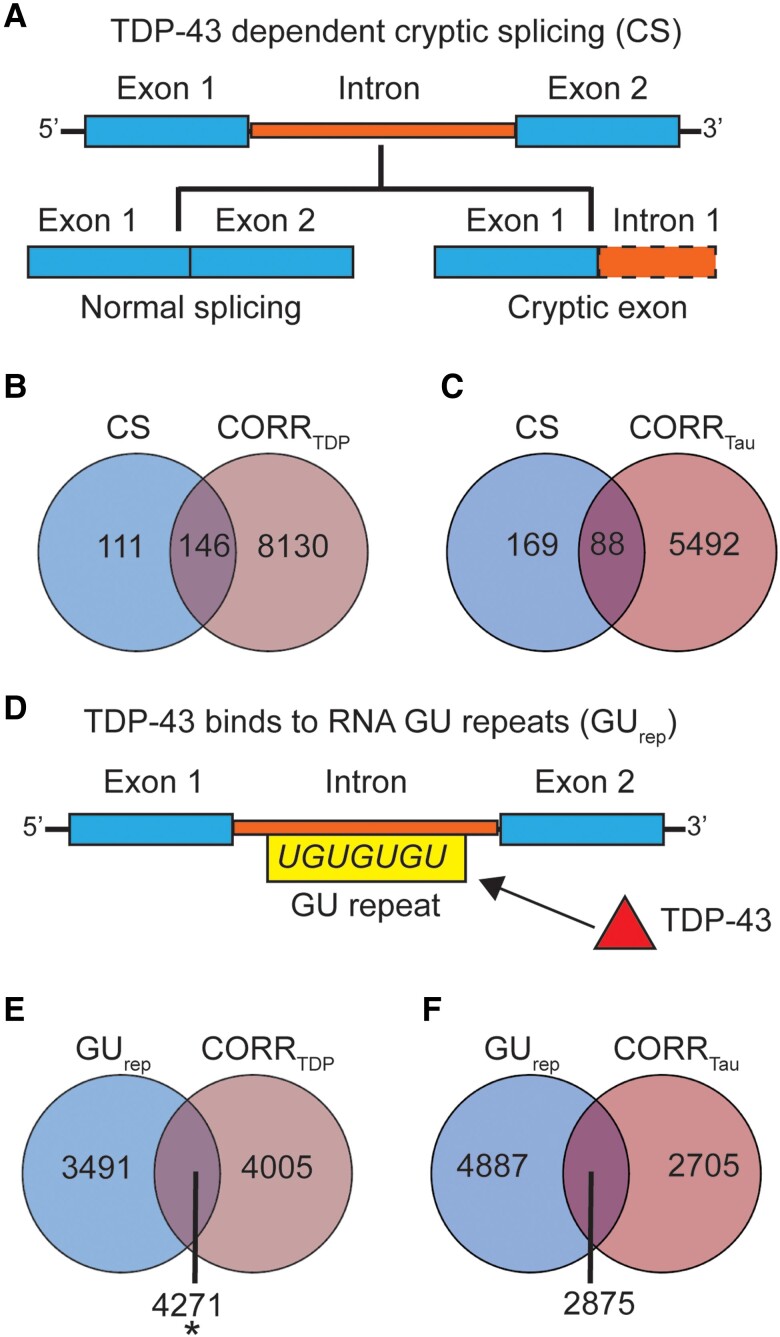
Figure 4.
Overlap between FTLD atrophy correlated genes and genes regulated by TDP-43. (A) Cryptic splicing (CS) genes are genes that incorporate novel intronic RNA into mature mRNA when TDP-43 is knocked down experimentally or depleted from diseased neuronal nuclei. (B) One hundred and forty-six genes were shared between cryptic splicing genes and genes correlating with atrophy in FTLD-TDP. This overlap did not reach significance (P = 0.11). (C) Eighty-eight genes were shared between cryptic splicing genes and genes correlating with atrophy in FTLD-tau, with this overlap being far from significant (P = 0.75). (D) TDP-43 binds to GU repeats located on the intronic portions of the pre-messenger RNA. GU repeats are ubiquitous among brain-expressed genes, we hence identified a set of 7792 genes with above-median GU repeat content, increasing the likelihood that these genes are regulated by TDP-43. (E) Genes (n = 4271) were shared between genes with above-median GU repeat content and genes correlating with atrophy in FTLD-TDP. This overlap was significant (P = 0.03). (F) Genes (n = 2875) were shared between genes with above-median GU repeat content and genes correlating with atrophy in FTLD-tau, with this overlap being not significant (P = 0.13). *P < 0.05. FTLD = frontotemporal lobar degeneration.