Figure 5.
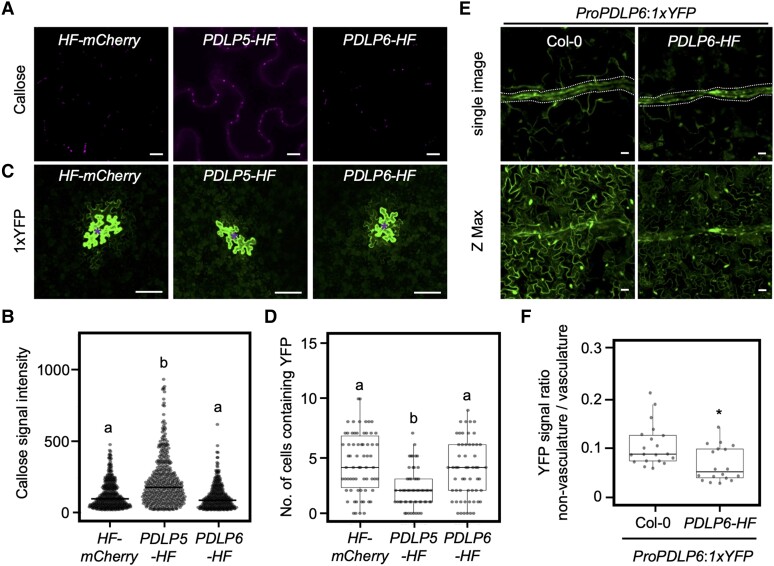
PDLP5 and PDLP6 regulate plasmodesmal function at different cell interfaces. A) Plasmodesmal callose accumulation in N. benthamiana leaves transiently overexpressing HF-mCherry, PDLP5-HF, or PDLP6-HF. Confocal images show aniline blue–stained callose between epidermal cells. Scale bars = 20 µm. B) Quantitative data present plasmodesmal callose accumulation. Each dot represents an aniline blue–stained callose. The box plots show the mean with Sd. HF-mCherry, n = 425; PDLP5-HF, n = 428; and PDLP6-HF, n = 362. The number of images used for quantification is as follows: HF-mCherry, 13; PDLP5-HF, 12; and PDLP6-HF, 14. Images were captured from 3 leaves. Different letters on the bar indicate statistically significant differences analyzed with 1-way ANOVA (P < 0.0001). C) Plasmodesmata-dependent movement of YFP in N. benthamiana leaves transiently overexpressing HF-mCherry, PDLP5-HF, or PDLP6-HF. Confocal images show the diffusion of 1xYFP from the transformed cells (indicated by asterisks) to the surrounding pavement cells. Scale bars = 100 µm. D) Quantitative data present plasmodesmata-dependent movement of 1xYFP. Each dot represents an individual transformed cell. The box plots show the mean with Sd. HF-mCherry, n = 66; PDLP5-HF, n = 56; and PDLP6-HF, n = 57. Images were captured from 4 to 5 leaves. Different letters on the bar indicate statistically significant differences analyzed with 1-way ANOVA (P < 0.0001). E) The diffusion of YFP from the vasculature to mesophyll and pavement cells in leaves of Col-0 and PDLP6-HF expressing ProPDLP6:1xYFP. Signals were detected in cotyledons of 14-d-old seedlings. Scale bar = 20 µm. F) Quantification of the YFP signals diffused from the vasculature to the other cell types. Mean signal intensity was determined in the vasculature (dotted area) and nonvasculature near the leaf tip. The ratio between nonvasculature and vasculature was calculated. A cotyledon from each seedling was used for imaging. The box plots show the mean with Sd. Col-0, n = 20; PDLP6-HF, n = 18. The asterisk indicates statistically significant differences analyzed with a Mann–Whitney U test (*P < 0.05).