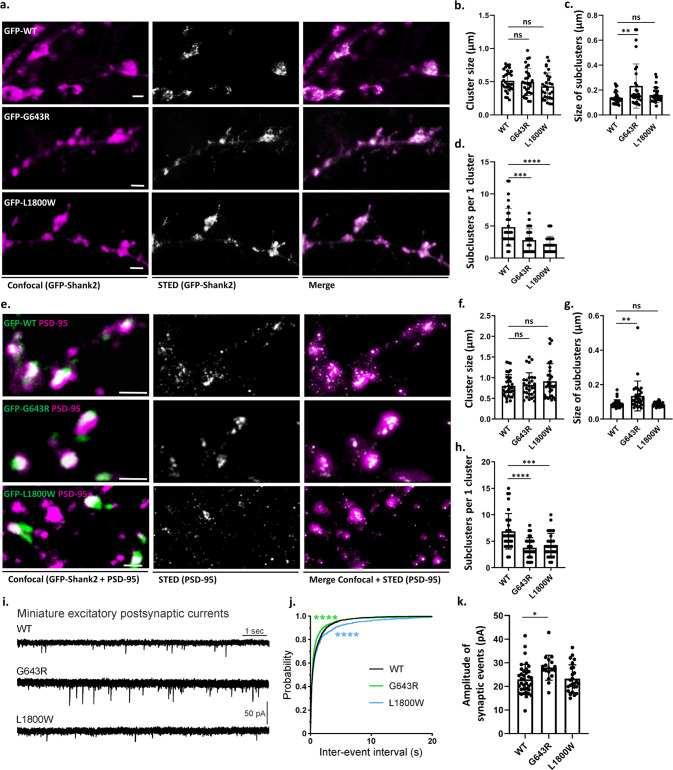
Fig. 5. Mutations in SHANK2 alter the nanoscale organization of both Shank2 and PSD-95 in the postsynaptic density.
Rat hippocampal neurons cotransfected with GFP-tagged human Shank2 constructs and a shShank2 vector, were stained with antibodies against GFP as well as PSD-95. Confocal and 2D STED imaging was performed on GFP-Shank2 clusters (a) or on PSD-95 clusters colocalising with Shank2 (e; areas of colocalisation are indicated in white, left panel). Single clusters of Shank2/PSD-95 observed in confocal mode were resolved into subclusters in super-resolution mode. Scale bar: 1 µm. Quantitative analysis was performed on 30 clusters from 10 neurons per each condition, obtained from three independent experiments. b The size of clusters in the confocal mode did not show any difference between WT Shank2 and the two mutant variants. c The size of Shank2 subclusters is significantly increased when expressing the G643R mutant compared to WT and L1800W. d Number of subclusters was significantly higher in clusters positive for WT Shank2 compared to both mutant variants. f The PSD-95 cluster size (confocal mode) was not significantly altered among the variants. g The size of PSD-95 subclusters was increased when expressing the G643R mutant compared to WT and L1800W. h Number of PSD-95 subclusters per cluster was significantly reduced for both mutant variants. **, ***, ****: significantly different, p < 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001 respectively; Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. i Miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) recorded in primary cultured hippocampal neurons cotransfected with shShank2 vector and human Shank2 construct. j Cumulative probability of mEPSC inter-event intervals was significantly altered for both variants. ****: p < 0.0001; Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. k The mean amplitude of mEPSCs was significantly larger in p.G643R variant cells compared to wild type cells. *p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.