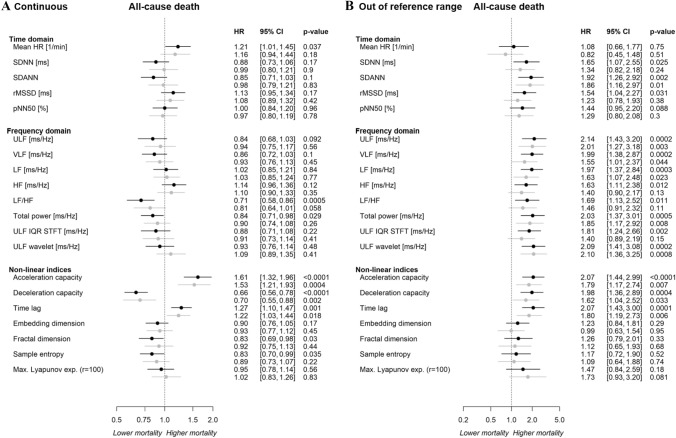
Fig. 5.
Relationship of HRV with all-cause death (A) as continuous trait and (B) for values outside of the reference range. Results of separate Cox regression models for each HRV parameter with adjustment for age and sex (black) and additional adjustment for traditional cardiovascular risk factors, comorbidities, and medication intake (grey) in the heart failure sample (N = 855). HRV is used as predictor and all-cause death as outcome with HRV as continuous trait (A) and for values outside vs. inside the reference range (B). HR, heart rate; SDNN, standard deviation of the NN intervals; SDANN, standard deviation of the 5 min average NN intervals; rMSSD, root mean square of the successive differences between normal heart beats; pNN50, percentage of neighboring NN intervals that differ from each other by more than 50 ms; ULF, ultra-low frequency; VLF, very low frequency; LF, low frequency; HF, high frequency; LF/HF, the ratio between low and high frequency; ULF IQR STFT, interquartile range of the ULF short time Fourier transform; ULF wavelet, median of the ULF wavelet transform; Max., maximal; exp., exponent; r, radius