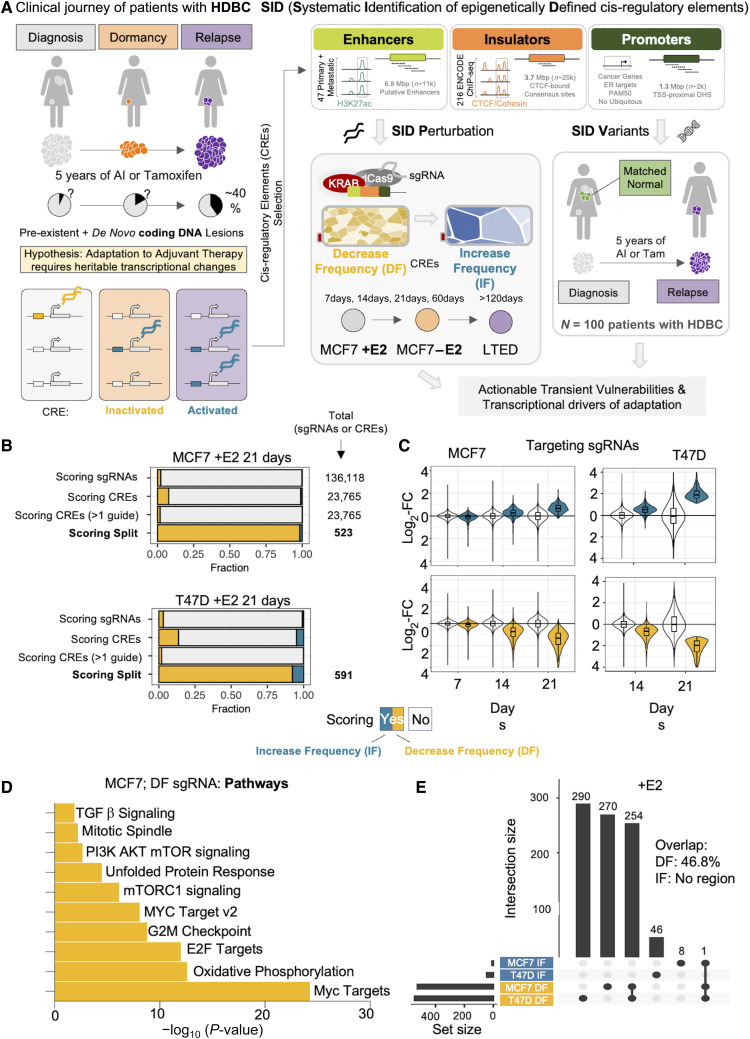
Figure 1.
Defining a comprehensive strategy to functionally annotate the noncoding genome of HDBC. A, HDBC journey is characterized by distinct phases. Cells must adapt to different niches and treatments. Overcoming these stresses require profound, heritable transcriptional changes. Leveraging in vivo and in vitro data we develop SID, a strategy to prioritize HDBC-specific regulatory regions for functional (SID Perturbation) and genomic (SID Variants) annotation in cell line models and in patient samples. B, Bar plot showing the relative fraction of scoring sgRNAs and CREs bearing scoring sgRNAs, upon perturbation of noncoding genome of estrogen dependent MCF7 cells via SIDP. Scoring sgRNAs showing a significantly decreased frequency at 21 days postinfection are referred to as DF, whereas those with a significantly higher frequency as IF. C, Box plots showing the log2 fold change of both scoring (either blue or yellow) and nonscoring (white) sgRNAs at 21 days postinfection in estrogen-dependent MCF7 cells, at 7, 14, and 21 days, as compared with the initial library. D, Bar plot showing the top 10 hallmark gene sets enriched among the genes found in the proximity of the CREs with scoring sgRNAs showing a DF pattern at 21 days postinfection (P value estimated via hypergeometric test). E, UpSet plot showing the intersection between the SIDP loci showing two or more concordant significant sgRNAs after 21 days postinfection, in either MCF7 or T47D cells (+E2).