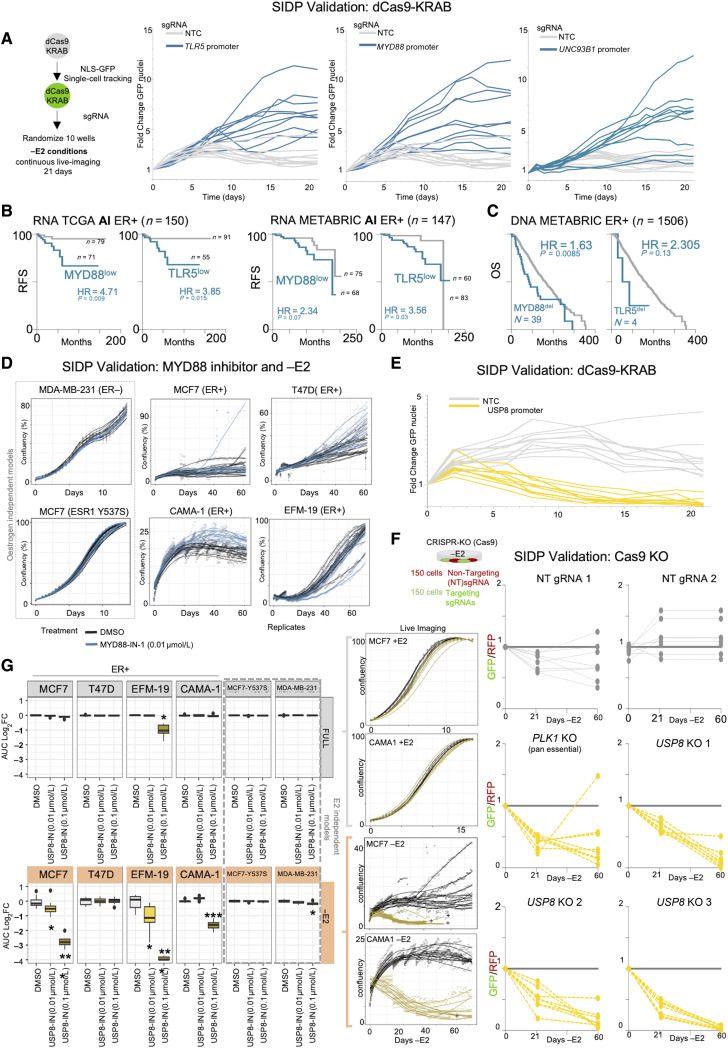
Figure 3.
Targeted CRE perturbations facilitate or disturb the adaptive processes. A, Overview of the experimental design. A, Cell growth dynamics of MCF7 cells under estrogen deprivation (−E2) were monitored by tracking the total number of GFP-positive nuclei with continuous live imaging over the course of 21 days. Cells carrying sgRNA for MYD88, TLR5, and UNC93B1 have a significant higher chance of avoiding therapy induced dormancy B and C, Retrospective patient stratification based on RNA expression (B) or CNVs (C) for MYD88 and TLR5. Log-rank P values calculated with a Mantel–Cox test. D, Cell growth dynamics for a panel of estrogen dependent (MCF7, T47D, CAMA1, and EFM-19) and estrogen independent (MDA-MB231 and MCF7 Y537S) breast cancer cell lines under estrogen deprivation (−E2) were monitored with continuous live imaging over the course of 60 days in presence of a low dose of MYD88 inhibitor (MyD88-IN-1). Chemical MYD88 perturbation increased the number of dormant persister and in turn the chances of early awakening. The same concentration did not have any significant effect in +E2 condition. E, Same as A but targeting the USP8 gene promoter. Cell growth dynamics of MCF7 cells under estrogen deprivation (−E2) were monitored by tracking the total number of GFP-positive nuclei with continuous live imaging over the course of 21 days. Cells carrying sgRNA for USP8 have a lower chance of adapting to therapy. F, CRISPR-Cas9 knockout of USP8. FACS sorting was used to quantify green (USP8 sgRNAs carrying cells) and red (nontargeting sgRNAs). FACS analyses were carried out at three specific timepoints. G, Cell growth dynamics for a panel of estrogen dependent (MCF7, T47D, CAMA1, and EFM-19) and estrogen independent (MDA-MB231 and MCF7 Y537S) breast cancer cell lines under estrogen deprivation (−E2) were monitored with continuous live imaging over the course of 60 days in presence of low dose of USP8 inhibitor (DUB-IN-2). Area under the curve during the entire length of experiment was compared with the average of the controls to quantify the overall impact of USP8 inhibition. Chemical inhibition of USP8 significantly impact the survival of cells adapting to long term −E2 conditions. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001; ***, P <10−5 (Mann–Whitney test).