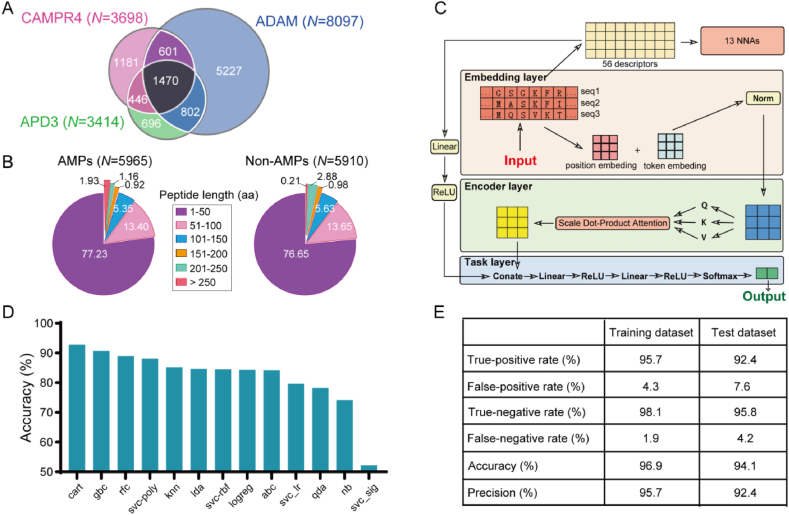
Figure 2.
Construction of the COMDEL model. (A) The venn diagram illustrates the AMP data collected from three AMP databases including CAMPR433, ADAM17 and APD315. (B) The pie chart displays the length distribution of the collected AMP and non-AMP data. (C) The COMDEL model consists of four main parts. The first is the ‘Embedding Module’, where each part of a protein sequence is turned into multiple data points based on its context. These data points are then standardized. Next, the ‘Encoding Module’ uses a special technique to understand complex sequence patterns, ensuring maximal utilization of every sequence portion. The third part, ‘Physicochemical Property Extraction’, pulls out 56 unique characteristics from the sequences, and these characteristics are processed using 13 different machine learning models. After these processes, their outcomes are merged with those the Encoding Module. Lastly, the ‘Task-Specific Module’ uses a group of neural networks to refine this information, turning it into probabilities for different categories. (D) AMP prediction accuracy comparison of the COMDEL model across 13 NNAs. (E) The AMP prediction performance of the COMDEL model in training and test datasets.